Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
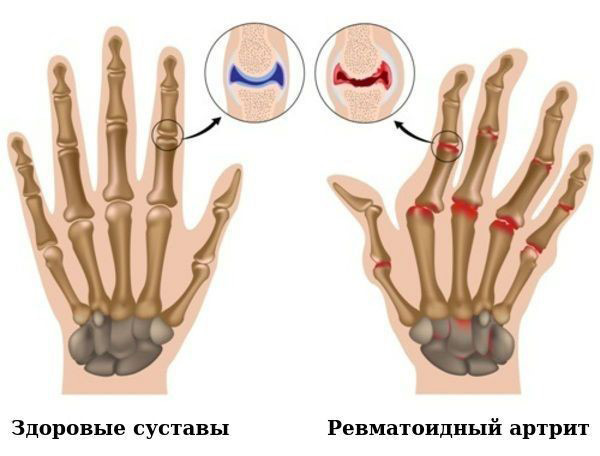
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease of the connective tissue with a predominant lesion of small joints, similar to erosive-destructive polyarthritis of unclear etiology. It is not associated with an infection, but with disorders in the immune system. This disease is called systemic, as the connective tissue is affected. Joint damage occurs due to chronic inflammation of the synovium, the inner layer that lines the joint capsule. In addition to joints, it can also affect internal organs (heart, blood vessels, kidneys) - these are extra-articular manifestations of the disease.
The disease is characterized by high disability (70%), which occurs quite early. The main causes of death from the disease are infectious complications and renal failure.
Causes of the disease
The causes of the disease are not known.
As with most autoimmune diseases, there are 3 main factors (rheumatological triad):
- genetic predisposition
- Hereditary tendency to autoimmune reactions.
- More common in carriers of a certain class MHC II antigen: HLA - DR1, DR4
- infectious factor
- paramyxoviruses - viruses of mumps, measles, respiratory syncytial infection
- hepatoviruses - hepatitis B virus
- herpesviruses - herpes simplex viruses, herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus, etc.
- Trigger factor: hypothermia, constant stay in a damp room or in a damp climate; hyperinsolation, intoxication, mutagenic drugs, endocrinopathies, nervous strain, stress injuries, joint diseases, etc.
Pathogenesis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease. This group of diseases is characterized by a change in the behavior of defender cells - lymphocytes. The cells of the immune system, instead of destroying foreign viruses, bacteria, fungi, begin to attack their own tissues and organs of the body, causing inflammation.
Clinical manifestations
Rheumatoid arthritis progresses in three stages.
In the first stage, periarticular edema of synovial bags occurs, accompanied by pain, local fever and swelling around the joints.
The second stage is the rapid division of cells, leading to the compaction of the synovial membrane.
In the third stage, the inflamed cells release an enzyme that attacks bones and cartilage, resulting in deformity of the damaged joints, increased pain, and loss of movement.
The onset of the disease in most cases is subacute and may occur after an infection, hypothermia, trauma or nervous strain.
One of the first symptoms is the appearance of stiffness in the morning, passing during the day. Also, a slight increase in body temperature, weakness, malaise, unexpressed, passing, and then constant pain in the affected joints. A slight swelling appears in them, which can pass during the day, but then becomes permanent.
In most cases, a small number of joints in the feet and hands are affected first. At an early stage, the knee joints may be involved. The lesions are symmetrical. With a subacute course, the first signs of disturbances appear after a few weeks, with a slow, chronic course - after a few months. Acute onset, high activity of the pathological process is characteristic of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in children and adolescents. It can begin with a high temperature, damage to several joints at once, and signs of damage to internal organs.
During the height of the disease, rheumatoid arthritis is accompanied by signs of general intoxication: weakness, malaise, slight fever, headache, lack of appetite, loss of body weight.
Articular syndrome is characterized by the presence of morning stiffness for more than 30 minutes and similar manifestations in the second half of the night - symptoms of "tight gloves", "corset"; constant sudden pain in the joints, aggravated by active movements. The disappearance of stiffness depends on the activity of the process: the greater the activity, the longer the duration of stiffness. Articular syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by monotony, duration, persistence of residual effects after treatment.
First, the small joints of the hand are affected, and then the large joints (shoulder, knee). They swell, become very painful, gradually lose their function, immobilize, which leads to severe atrophy (reduction in volume) of the muscles. Lesions of different joints may be different: in some, signs of inflammation (edema) may prevail, in others - proliferation (growth of connective tissue with deformity and dysfunction).
Small subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules appear - moderately dense, painless formations located on the surface of the body, most often on the skin of the elbows. The peripheral nervous system is affected: patients feel numbness, burning, chilliness in the limbs. In rheumatoid vasculitis, various small and partially medium-sized blood vessels are affected. Often this manifests itself as pinpoint foci of necrosis in the area of the nails or painless ulcers in the shin area. Sometimes vasculitis can manifest itself in the form of microinfarcts.
Rheumatoid arthritis is often combined with other joint diseases - osteoarthritis, rheumatism, systemic diseases of the connective tissue
With the progression of rheumatoid arthritis, the internal organs are affected:
- hearts - endocarditis, pericarditis, atherosclerosis;
- kidneys - amyloidosis, nephritis;
- lungs - pleurisy, nodular lesion of the lung tissue;
- organs of vision, etc.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of this disease appear, you should consult a doctor. The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is confirmed by additional examination data.
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis includes:
Laboratory research:
- general blood test - reveals the inflammatory process (ESR accelerates, the number of leukocytes changes);
- biochemistry - allows you to clarify the causes of inflammation and metabolic disorders;
- immunological studies - the presence or absence of specific antibodies.
Instrumental research:
- reveals the pathology of the joints X-ray diagnostics;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging (CT, MRI) - allow for the assessment of early articular changes;
- Ultrasound - reveals an increase in the volume of joint fluid and the presence of areas of necrosis.
Treatment
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis begins with the elimination of inflammation and pain. Then a complex treatment is added, which includes:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- therapeutic exercises and massage;
- surgical methods of treatment.
There must be a balanced diet: the diet should contain foods rich in calcium (cottage cheese, cheese, kefir), vegetables, fruits, vegetable soups, lean meat and fish.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis is divided into two stages:
- The first stage includes the relief of the acute phase of the disease
- The second stage is maintenance therapy
Treatment of the acute phase is to reduce the inflammatory process.
This is an individually selected therapy, which includes the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoid drugs (GCS), basic drugs and biological agents.
At the same time, physiotherapy is prescribed, the main goals of which are:
- Correction and prevention of the development of functional disorders;
- Reducing prolonged pain and swelling;
- Normalization of local blood flow and tissue nutrition;
- Prevention of atrophy of muscles and ligaments;
- Improving overall well-being, performance and quality of life.
In the acute period of the disease, two types of physiotherapeutic treatment are used: exposure to ultraviolet radiation and electrophoresis of glucocorticoids on the area of \u200b\u200bthe diseased joint.
Most often, physiotherapy for arthritis is carried out after the symptoms of exacerbation have been eliminated. Treatment is prescribed individually in accordance with the age of the patient, his general condition, the presence of complications and concomitant diseases.
In the remission stage, the following are prescribed: UHF, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis with dimexide, EHF therapy, balneotherapy, mud therapy, acupuncture, Lyapko application therapy, massage, visceral massage of the abdomen according to Ogulov A.T. (massage of internal organs through the anterior abdominal wall), lymphatic masses of the abdomen according to Shishova O.I. and etc.
If there are no contraindications, courses of physiotherapy are repeated every 5-6 months.
Application therapy Lyapko
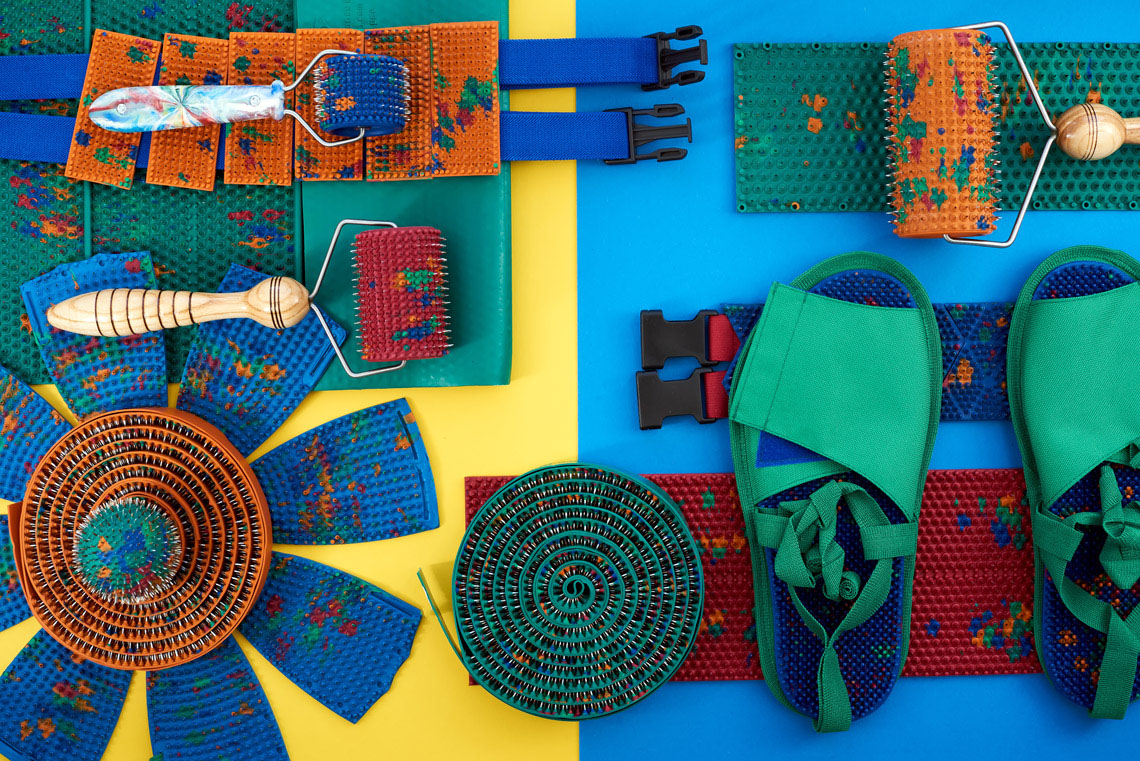
Lyapko's applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, applique belts, applique tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic possibilities.
Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
Mechanisms of action of the applicator
The high healing effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvano-electric;
- immunological.
Application therapy has a pronounced analgesic and antispasmodic effect. Improves blood circulation, lymph flow, microcirculation, reduces tissue swelling. It activates tissue mechanisms of immune defense, increases the level of its own opiate peptides and anti-stress hormones in the blood, reduces the sensitivity of pain receptors, has a positive psycho-emotional effect and, as a result, stimulates the general adaptive mechanisms of a person. In contact with the skin, the applicator needles stimulate the release of a person’s internal medicines, including his “inner doctor” in his work.
Applicators are widely used in medical institutions, health centers and sanatoriums. Ease of use, safety, high efficiency with minimal effort allow us to recommend applicators for self-use at home.
It is important to note that the local (local) improvement of patients and, especially, those with coronary heart disease, circulatory failure of 1-2 degrees, elderly people. this is the time to rest. This is very important for all categories.
Many patients are contraindicated in electrophysiotherapy procedures for various reasons. These are elevated blood pressure figures, the presence of metal in the body (knitting needles, metal fragments), pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, etc. In these cases, Lyapko's application therapy is the means of choice.
With pain in the joints, patients show positive dynamics from Lyapko's application therapy, which is compatible with all types of medical and physiotherapeutic treatment.
The therapeutic effect of applicators is enhanced if they are applied to the skin, previously moistened with water, hypertonic solution or gauze with a decoction of medicinal herbs, water-based drugs. After removing the applicator, all the pores of the skin at the site of its application are opened and the application of therapeutic oils, ointments and compresses is most effective.

How to work with the applicator, application zones
If the problem is associated with damage to the joints of the upper extremities, then it is necessary to act with applicators on the cervical-collar spine, from where the innervation to the upper extremities comes, then on the joint area.
If there are problems in the joints of the lower extremities, then you need to apply applicators to the lumbosacral spine, from where the innervation to the lower extremities comes, then to the joint area.
You can act simultaneously or sequentially.
When attaching a lesion to the internal organs, application therapy is applied to the zones of correspondence to these organs on the back and on the front surface of the body.
Important! Since a common cause of all autoimmune diseases are infectious diseases of the intestines or the genitourinary system, it is imperative to restore the movement of lymph and blood in the abdomen.
Lyapko's application therapy is indicated to improve the functioning of the abdominal organs, intestines, where the largest amount of lymphoid tissue is located, which is responsible for the functioning of the immune system.
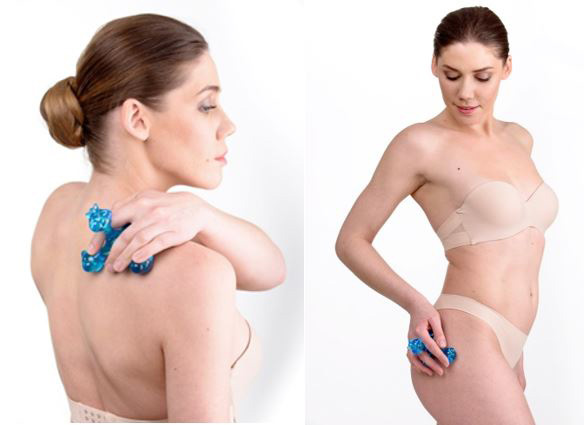
To do this, it is recommended to use flat applicators on the lower thoracic and lumbosacral spine, additionally on the auxiliary zone - the anterior abdominal wall (simultaneously or alternately), you can also wrap these zones with the "Health Magic Tape" for 20-30 minutes or roll these areas with application rollers for 10-15 minutes.
Lyapko application therapy is used both as an independent procedure and as a preparation for relaxing the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall for visceral massage of the abdomen.
These procedures improve the functioning of internal organs, relieve congestion, inflammation in them, restore the functioning of the lymphatic system, and increase immunity.

It is recommended to use flat applicators on the back area: Applicator "Large mat" , "Massage needle large mat" , "Chance 6.2x4" .
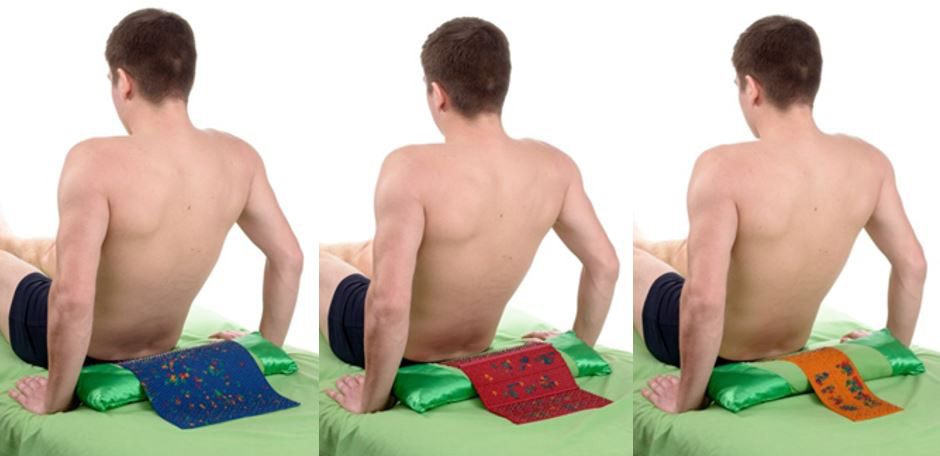

Flat applicators "Chamomile M" , "Quadro" , "Duet" , "Chance" , "Folk" , placing them both along the spine and across.

In addition to the back area, to enhance the effect, it is recommended to use applicators simultaneously or alternately on auxiliary areas: on the front surface of the abdomen, torso. The use of applicators on the area of the kidneys, adrenal glands (under the control of blood pressure - do not use at elevated pressure), on the abdomen improves the functioning of the immune system. The exposure time is 20–30 minutes, the course of treatment is 10–14 days, which can be repeated after a break in 1–2 weeks. Such procedures can be applied in courses for a long time.
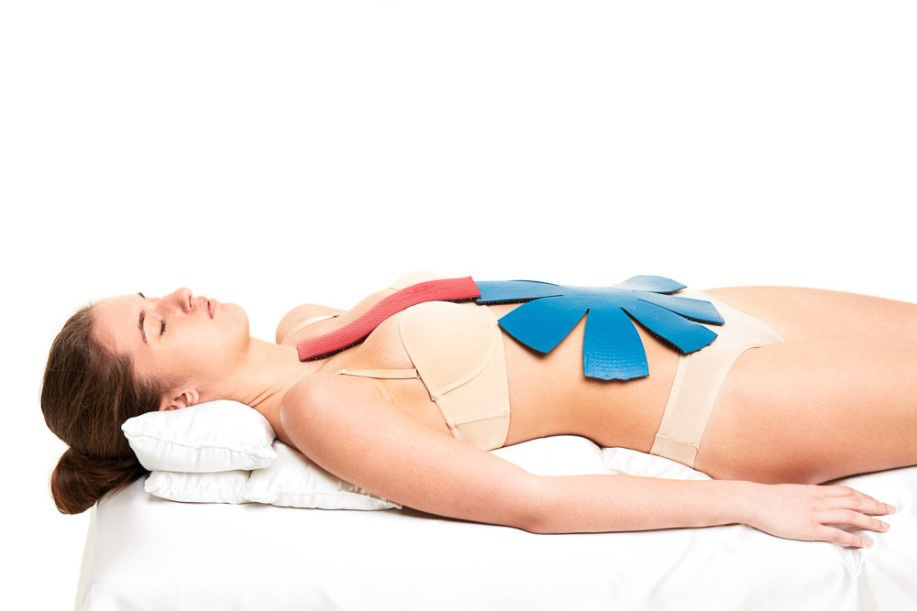

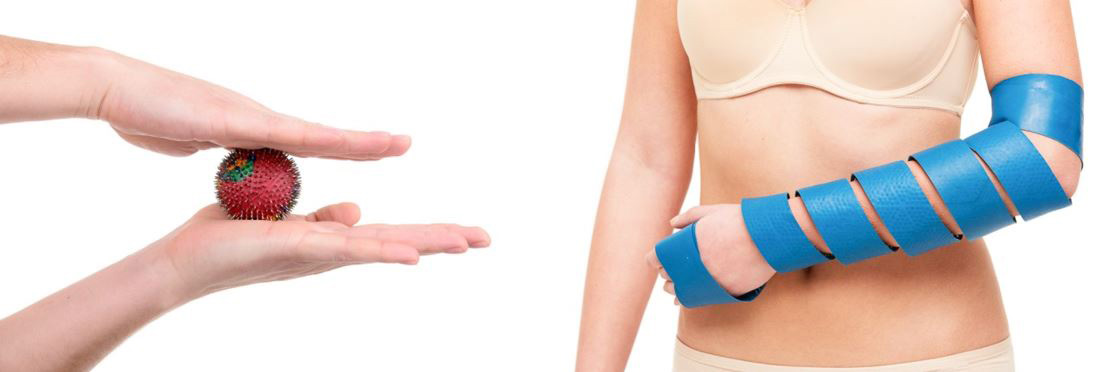
The applicator "Chamomile M" is especially convenient to use , which, thanks to its flexible "petals", acquires the relief of any part of the body. They can have an impact on any part of the spine, hip and knee joints (fixed with an elastic bandage); apply to calves, feet. The exposure time with flat applicators is 20-30 minutes.
You can also use static-dynamic applicators: "Magic tape "Health" , belt "Universal M" , belt "Baby" . Uniform pressure on the surface of the body and ease of fixation allows you to move freely, do the usual thing and at the same time be treated.
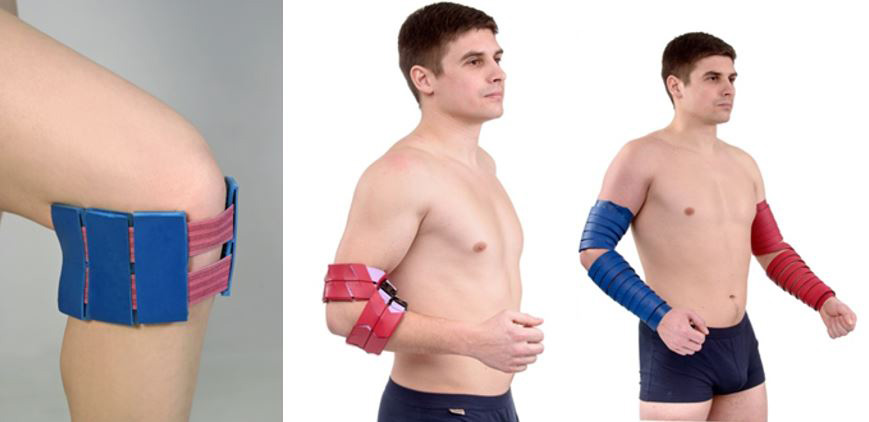

It is recommended to fix the applicator for 20-30 minutes to the areas of damaged joints; additionally, you can use the zones of the opposite healthy side for 10-15 minutes. The procedure time is 20-40 minutes, the course of treatment is 1-2 weeks, the treatment can be repeated after 2-4 weeks.
To relieve stiffness in the joints in the morning, fixation on the limb gives good results, starting with the fingertips of the Magic Tape "Health" , rolling along the palmar and back surface of the hand with the "Needle Ball" or application rollers.
There is a positive practical experience of long-term, for several months in a row, daily use of applicators. There was a persistent improvement in well-being, removal of chronic pain, increased vitality and performance.
In addition or before the massage, it is possible to treat painful and adjacent areas using the “Large Roller M” or “Universal Roller M” . The exposure time is 3–7–10 minutes, depending on the individual skin reaction (until a uniform pink color appears).
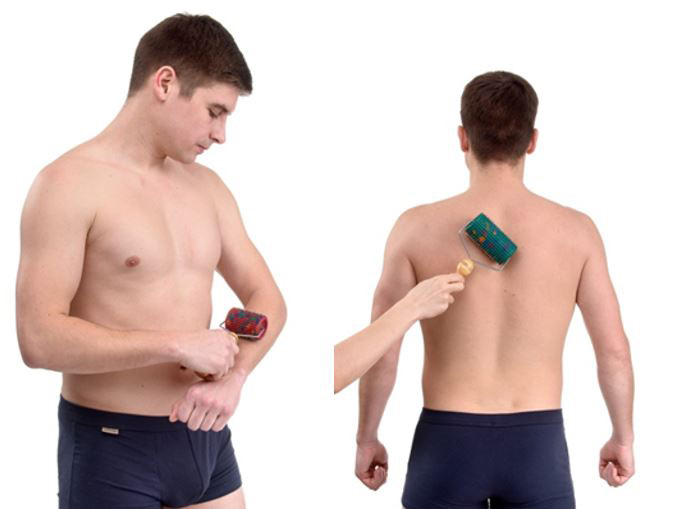

It is also necessary to massage the upper and lower extremities, the corresponding zones of the spine, the joint, for example, using the Pharaoh massager , but at the same time, direct exposure to the diseased joint should be avoided, as this can increase the inflammatory reaction in it, work above and below the joint .
It is very effective to act on the feet using the application "Insoles Plus" , or other types of flat applicators, as well as rollers. There are biologically active points on the feet - projections of all organs and systems. The impact on them with applicators contributes to the restoration and normalization of the function of all organs and systems. Insoles can be used on other parts of the body.

