Osteoporosis
2 Most common fracture sites in osteoporosis
3 Signs of the development of the disease
7 The use of Lyapko application devices
What is osteoporosis
The decline in deaths from infectious and cardiovascular diseases worldwide over two decades has led to life expectancy. Symmetrically to life expectancy, the number of people suffering from diseases of the musculoskeletal system increases.
Some age-related changes in the body are inevitable. Scientists say that you should not be afraid of old age. If you regularly engage in physical activity, such as exercising, walking, eating right, you can maintain the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system even in old age.
Osteoporosis is a chronic, systemic, metabolic disease that is characterized by a decrease in bone mass and structural changes, leading to increased bone fragility and the risk of fractures. Osteoporosis develops gradually and is clinically detected, as a rule, after fractures, which served as the basis for calling it a “hidden epidemic”.
According to the World Health Organization, osteoporosis, as a cause of disability and mortality, ranks fourth in the world after such diseases as cardiovascular, oncological and diabetes mellitus.
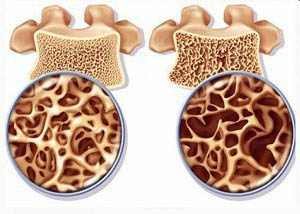
With osteoporosis, the bones become porous like a sponge, there is a progressive decrease in bone density, as a result of which their strength is significantly reduced. This disease affects all the bones of the skeleton at the same time, which leads to the risk of fractures in the simplest life situations, with the most ordinary loads.
Our bones contain minerals, in particular calcium and phosphorus, which give bones their hardness and density. Osteoporosis is characterized by a decrease in the content of these minerals in all bones of the skeleton, due to their "washout". The reason for this is hormonal disorders and metabolic disorders.
Bones and joints in osteoporosis are subject to deformation from the weight of their own body. The vertebrae often become flattened and wedge-shaped. The rounded heads of the hip joints become oval, oblique. Deformities of the knees and ankle joints, progressive flat feet are possible.
There are so-called pathological fractures - these are fractures due to increased fragility of the bone. For such a fracture, the weight of one's own body or one awkward movement is enough.
Vertebral fractures are usually asymptomatic until they lead to compression of the spinal cord or nerve.
Often there is a pathological fracture of the femoral neck.
Most common fracture sites in osteoporosis
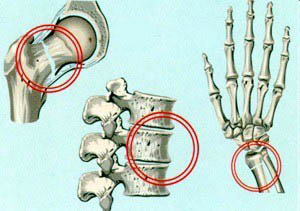
Studies have shown that every third woman and every fifth man over 50 suffer from this disease.
There are two main types of osteoporosis:
- Primary (independent disease) develops, as a rule, after 50 years.
- Secondary osteoporosis is a manifestation of some other disease, most often the result of a violation of metabolic or hormonal processes in the body.
Signs of the development of the disease
- General weakness, fatigue, night cramps, early gray hair, heart palpitations, periodontal disease and plaque, delamination and fragility of nails.
- Pain in the lumbar and sacral spine, in the ankle and hip joints, pelvic bones. Pain is aggravated after a small physical activity and a long stay in one position.
- Intervertebral hernias.
- Heaviness in the interscapular region and general muscle weakness.
- Decrease in height by more than 1–1.5 cm, deterioration in posture and curvature of the spine.
- Most patients with osteoporosis complain of a significant decrease in performance and increased fatigue.
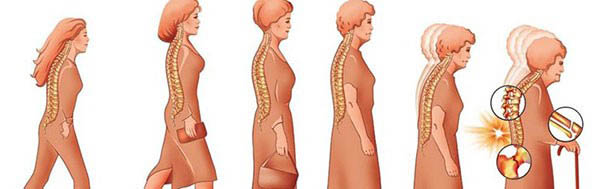
Main reasons
The main causes that can lead to the development of osteoporosis are:
- Hormonal changes that occur during menopause, against the background of a decrease in estrogen levels. Women suffer from fractures three times more often.
- Dysfunction of the ovaries, as well as other endocrine glands.
- Insufficient physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle, as bone density directly depends on the physical load on the bones.
- Malnutrition and abuse of restrictive diets
- The use of medications (usually hormonal).
- Violation of digestion, functions of the thyroid and pancreas
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, allergies and other diseases associated with metabolic disorders and salt metabolism.
- Long-term use of hormonal drugs.
- The presence of the disease in one of the relatives (genetic predisposition).
Treatment of osteoporosis
Currently, four options for the treatment of osteoporosis approved by the World Health Organization (WHO) are generally accepted:
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Bisphosphonates (bisphosphonates)
- Calcitonin
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators
Drugs can be taken only as prescribed by the attending physician!
But the best option should be the prevention of osteoporosis.
The value of the use of physiotherapeutic procedures for the prevention of osteoporosis, with osteoporosis, with fractures.
Physiotherapy treatment is carried out to improve blood supply, relieve the severity of pain. The following types of physiotherapy are used: magnetic therapy, ultrasound with hormonal preparations, electrophoresis with novocaine, laser therapy, Lyapko application therapy, mud therapy, paraffin therapy, etc.
A properly selected set of procedures not only promotes recovery, but also reduces the drug load on the body.
The use of Lyapko application devices
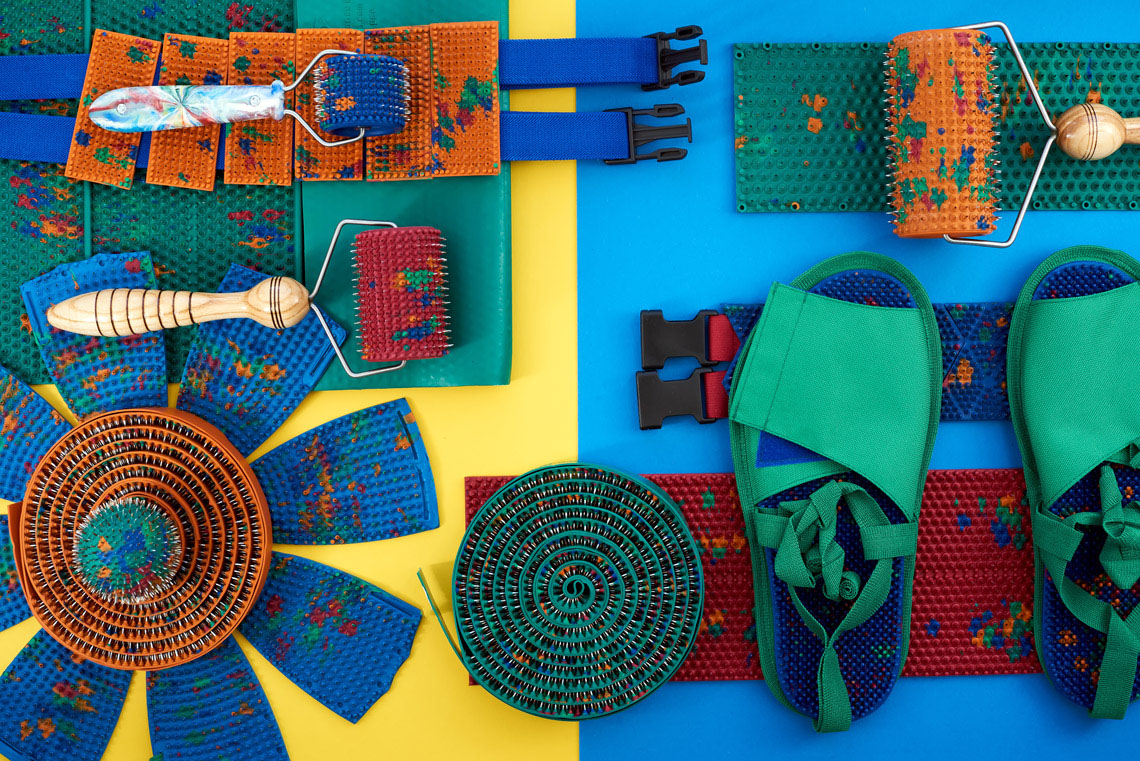

Lyapko's applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, applique belts, applique tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic possibilities. Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
Mechanisms of action of the applicator.
The high healing effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvano-electric;
- immunological.
The clinical effects of the method of multi-needle therapy are manifested in analgesic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, neurotrophic and immunomodulatory effects. Also in the regulation of the functions of the autonomic nervous system, the normalization of the processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system.
Lyapko's application devices are among the methods of physiotherapeutic treatment, improve blood circulation, microcirculation and transcapillary metabolism, increase blood supply to organs and tissues, and reduce inflammation in them.
All metabolic processes in the body are activated, which is especially important for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis. Applicators are widely used in medical institutions, health centers and sanatoriums.
Compatible with all physiotherapy procedures. Ease of use, safety, high efficiency with minimal effort allow us to recommend applicators for self-use at home.
How to work with the applicator, application zones
In 90% of cases, it is necessary to act on the pain zone, and to increase efficiency on additional and auxiliary zones.
It is always necessary to include the main zone (the region of the spine) in the general recipe.
Additional and auxiliary zones should be used when, for a number of reasons, it is impossible to influence the main zone (gypsum is applied, the wound surface). To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is advisable to include in the formulation the effect on the symmetrical zones of the healthy side.
The main zones are located on the back surface of the trunk, head, neck.
The main ones are named due to the fact that the skin areas on both sides of the spine and directly above the spine are closest to the exits of the roots of the cranial and spinal nerves and other structures.
Auxiliary zones: front surface of the trunk, head and neck.
Additional zones: zones of the skin of the lower and upper extremities, which are secondary (peripheral) in relation to the (central) structures of the spinal cord and brain.
On areas of the body with a large radius of curvature: back, abdomen, chest area, lumbosacral region, arms, legs, palms and feet, use flat applicators for 15-30 minutes. You can use the following applicators: "Rug large" , "Chamomile M" , "Massage needle large mat" , "Chance 6.2x4" , "Quadro" , "Chance" , "Folk" , "Duet" , "Insoles plus" . The course of treatment is 10-14 days, after 2 weeks you can repeat the procedure. If you want, you can carry out the procedures daily, listen to your body.

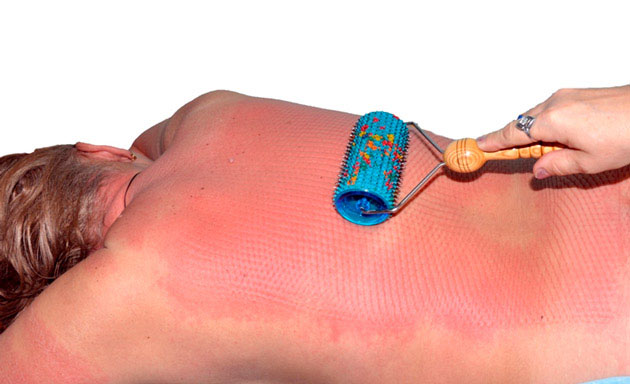
It is recommended to massage the whole body with the Pharaoh massager, the exposure time is 10-15 minutes; running in the back with “Large Roller M” , “Universal Roller M ” until a slight reddening of the skin appears (5–10 minutes, depending on skin reaction), or laying on large flat applicators for 30–40 minutes.
 |
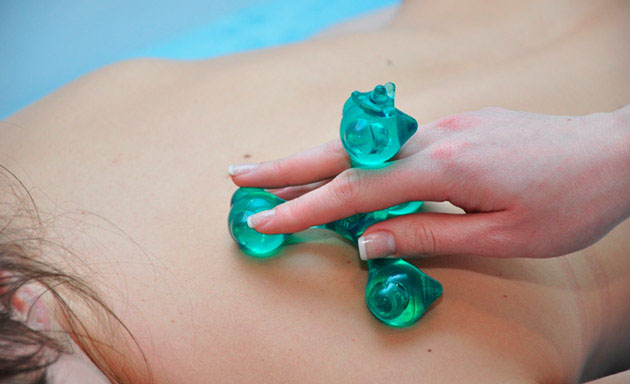 |
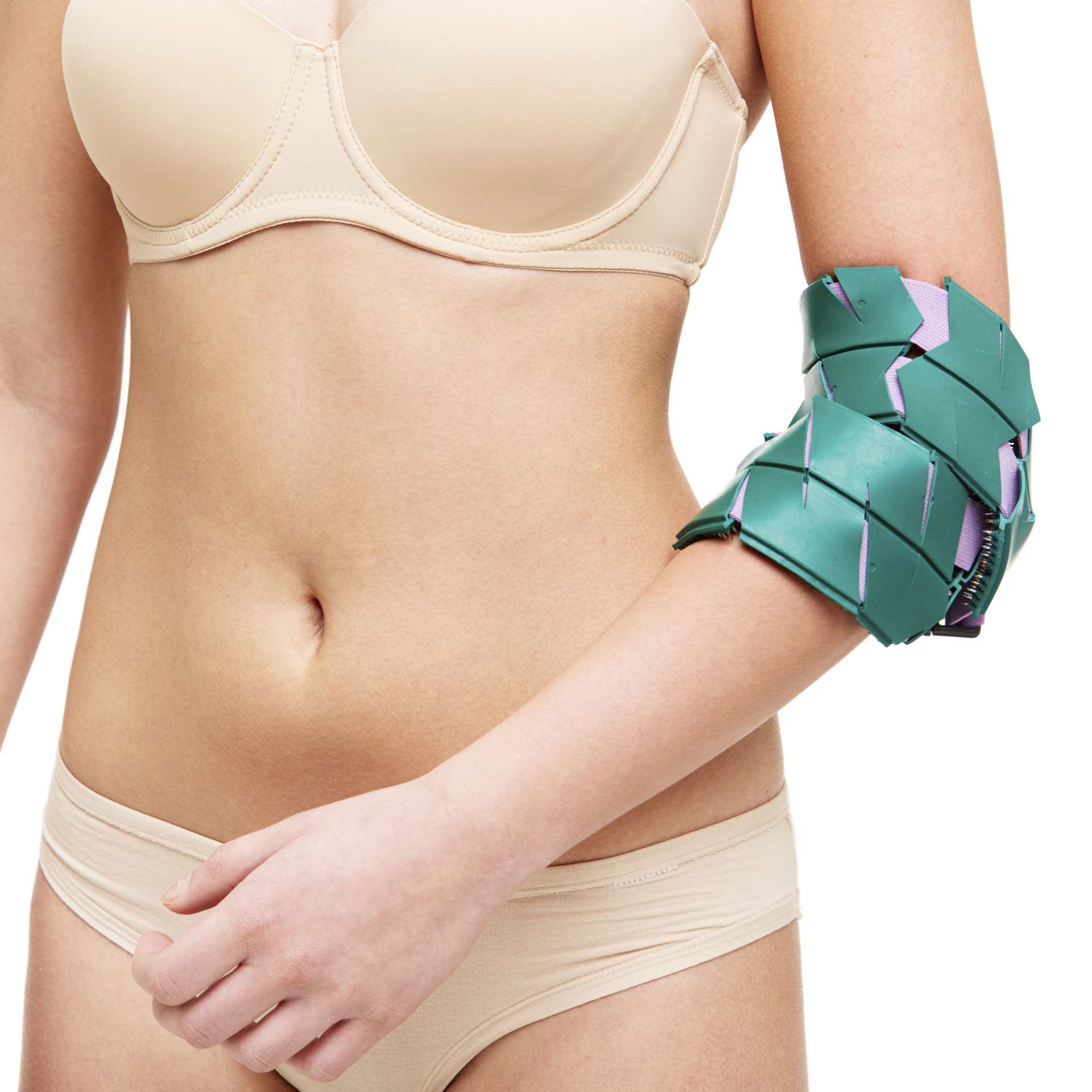
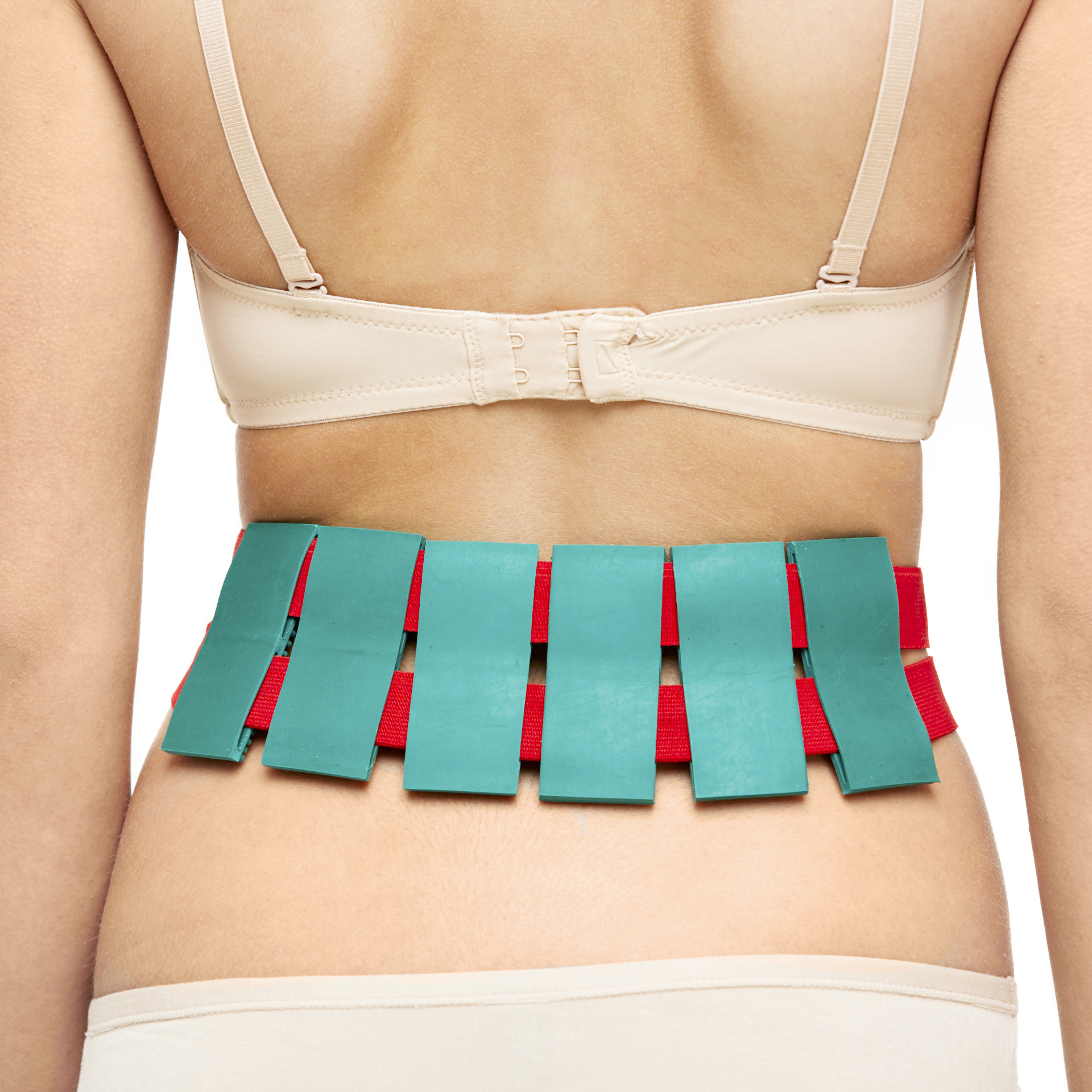
It is convenient to use the applicator "Chamomile M" on the joints , the belt "Kid" , the belt "Universal M" , "Magic Ribbon" Health " .
The combined use of flat Lyapko applicators, needle rollers and the Pharaoh massager mutually potentiates (increases) their therapeutic effectiveness.
 |
 |
Prevention
To maintain the musculoskeletal system in good condition, it is required to lead an active lifestyle throughout life: move, do exercises, spend more time in the fresh air, take sunbaths (1-3 hours a day). The lack of loads leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes in the body, a decrease in muscle mass, impaired mobility and endurance, and human weakness.

It was noticed that in women after 50-70 years old, regularly engaged in physical education, leading an active lifestyle, the state of bone and muscle mass corresponded to the level of a younger age.

For the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system in old age, physical activity (at least 45 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise 3 times a week) and proper nutrition are important.
Be sure to regularly do breathing exercises, physiotherapy exercises, massage and self-massage courses, and receive physiotherapeutic procedures. A good help at home is the Lyapko applicator.
Another important factor in the prevention of osteoporosis is a rational and balanced diet. The most important thing in the prevention of osteoporosis is a sufficient amount of calcium in the diet, which the body must receive throughout life, since bone loss begins as early as 30 years of age.
When taking calcium in the form of tablets or dietary supplements, it is necessary to combine it with vitamin D, since it helps the body absorb calcium. Calcium citrate is absorbed better than carbonate.
It should be borne in mind that calcium is poorly absorbed along with foods containing oxalic acid - these are spinach, gooseberries, currants, rhubarb, strawberries, chocolate, wheat bran, nuts, beets and tea.

Products useful for osteoporosis:
- All varieties of cabbage, especially broccoli, cauliflower.
- All types of nuts.
- Whole grain products.
- Dairy and sour-milk products (natural).
- Fish.
- Seaweed.
- All dried fruits, especially dried apricots and prunes.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits, herbs.

Women during menopause must eat plants containing phytoestrogens. There are more natural estrogens in traditional oriental cuisine. Perhaps that is why Eastern women endure menopause more easily.
