The foot is a particularly reflexogenic zone of our body
1 The sole of the feet and its features
2 The sole of the feet is a special micro-puncture zone
3 What you need to know about feet
4 General characteristics of the reflexogenic zones of the feet
5 Scheme of the main reflex zones of the feet
6 Additional reflex zones of the feet
8 Guidelines for the use of Lyapko application devices
10 Video. Foot massage. Projections of internal organs on the foot.
The sole of the feet and its features
The sole of the feet can rightly be called a special zone of the body. It contains a mass of skin receptors that make up the peripheral parts of the reflex apparatus, through which the internal organs and various systems of the body make contact with the external environment, by acting on which it is possible to treat the whole organism.
No species of animal, except monkeys, has arms and legs like humans. When the person "straightened up" and stood on both feet, the weight of the body moved to the soles and pressed them to the ground. The ancestor of modern man, running barefoot on uneven ground, received natural stimulation of the reflexogenic zones of the feet, which led to reflex excitations of certain parts of the brain; maybe that's why he started to develop faster? From that time to the present day, the human subconscious has learned to pay attention to the various sensations of the legs when they come into contact with the ground.
A system of healing and recovery of the body was developed and tested by influencing the soles when walking and running barefoot. The famous philosopher Socrates was a zealous supporter of walking barefoot. He believed that this leads to hardening of the body and sharpening of thoughts. The ancient Spartans even had a special rule according to which the wearing of shoes was allowed only after 18 years.
From the advent of foot protection to our modern footwear, our feet have moved further and further away from nature. Alas, the vast majority of modern adults have forgotten how to walk barefoot, and if so, they do not develop such a need in their children. Thus, the child is deprived not only of an additional opportunity for hardening, but also of a tonic or calming effect on certain body systems through the nerve endings of the surface of the feet.
The sole of the feet is a special micro-puncture zone
The foot is not only an organ designed for movement and support, but it is also a sensitive device for communicating with the world. The foot perceives not only temperature, humidity, hardness and other properties of the surface it steps on, but it has the properties of a special “vibration hearing”. Bare feet are able to pick up the smallest vibrations in the ground. On the soles and toes there are neuroprojective representations of the whole organism, all organs. Physiologists have proven that the sole is one of the most powerful reflexogenic zones, with more than 72,000 nerve endings. So, on 1 square centimeter of the sole, there are 1.5 times more mechano- and thermoreceptors than on the same surface of other parts of the body.
The plantar surface of the feet with good reason can be called a special micropuncture zone of the body. By acting on certain areas of the sole, it is possible to influence those parts of the body or internal organs that need treatment. Although it is possible to work on isolated areas of the feet, the desired effect is achieved only when both feet are treated. Covering all the reflex zones of the foot, the treatment becomes "holistic", since the effect occurs on the entire body. While this method seems simple, the results can be stunning!
What you need to know about feet
The main element of the foot is its arch. It is formed due to the special arrangement of the bones, which are held in the required position by numerous powerful ligaments. If the tension of the muscles and ligaments weakens, the arch of the foot drops, and its deformation occurs. Thanks to the arch, the foot is elastic, thanks to the joints and muscles, it is mobile. Untrained leg muscles are also the cause of numerous foot deformities.
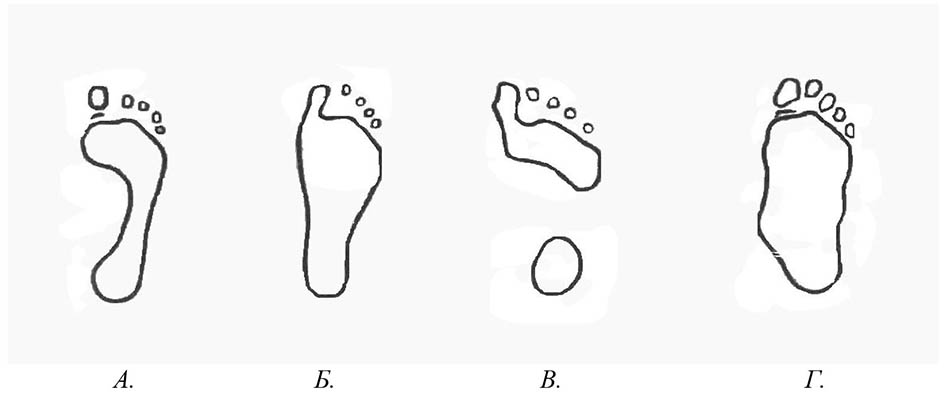
Figure 1. Types of feet. A - normal foot, B - flat foot, C - hollow foot, D - combination of flat feet with external clubfoot.
The consequences of flat feet are manifested in the state of the joints, sensations of the spinal column. Body weight is redistributed to the knee and hip joint to maintain the stability of the person. At the same time, depreciation functions of the spine are violated, which can lead to changes in the intervertebral discs: the appearance of hernias, cracks. Compression of the nerve endings is accompanied by constant pain in the buttocks and back, in the legs, in the internal organs, and headaches. Flat feet can lead to arthrosis of the knee joint, osteochondrosis, scoliosis, spondylosis, osteoporosis; vertebral artery syndrome leading to frequent headaches; heel spur; varicose veins, etc.
Feet in shoes are "chained" to the same surface all day long - the inner surface, the so-called block, therefore, as a rule, only negative reactions are produced in the reflexogenic zones, which can lead to diseases.
For prevention, it is important not to wear the same shoes all the time so that the foot does not get used to the block. There should be a lot of shoes, alternate different heel heights in order to maintain the elasticity of the muscles of the arch of the foot.
General characteristics of the reflexogenic zones of the feet
Each organ and part of the body has its own projection on the foot, and the location of the projections has a certain pattern. So, the feet brought together resemble a sitting human figure (Fig. 2)
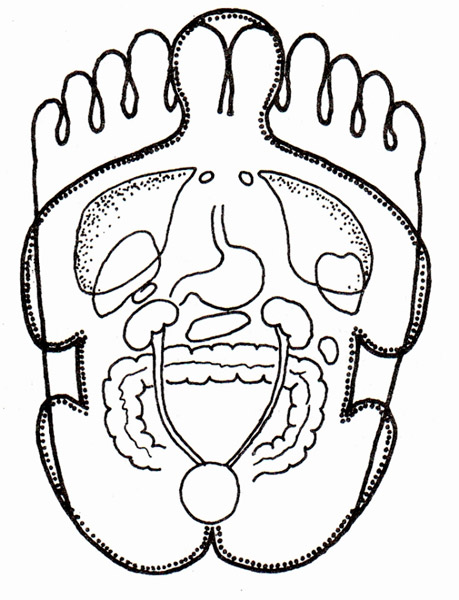
Fig. 2 The thumbs correspond to the projection of the head. The forefoot is like a chest with a heart and lungs. The middle part of the foot corresponds to the abdominal cavity, containing the stomach, intestines, pancreas, kidneys, liver, and gallbladder.
The right foot corresponds to the right side of the body, and the left to the left. Parts or organs of the body located on one side correspond to their foot, for example, the gallbladder will belong to the right, because it is located on the right side of the body, and the heart and spleen to the left. The heel is similar to the pelvic cavity and contains projections of the uterus, ovaries, prostate, testis, bladder, urethra, vagina, and anus.
The inner surface of the foot - the location of the spine (Fig. 3)
The depression at the medial edge of the foot is similar to the spinal column, including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx. The medial (inner) edge of the foot resembles the human torso and head when viewed from the side: the thumb corresponds to the head, the ball of the thumb to the back of the head, the base of the thumb to the neck, etc. The ankle corresponds to the hip joint.
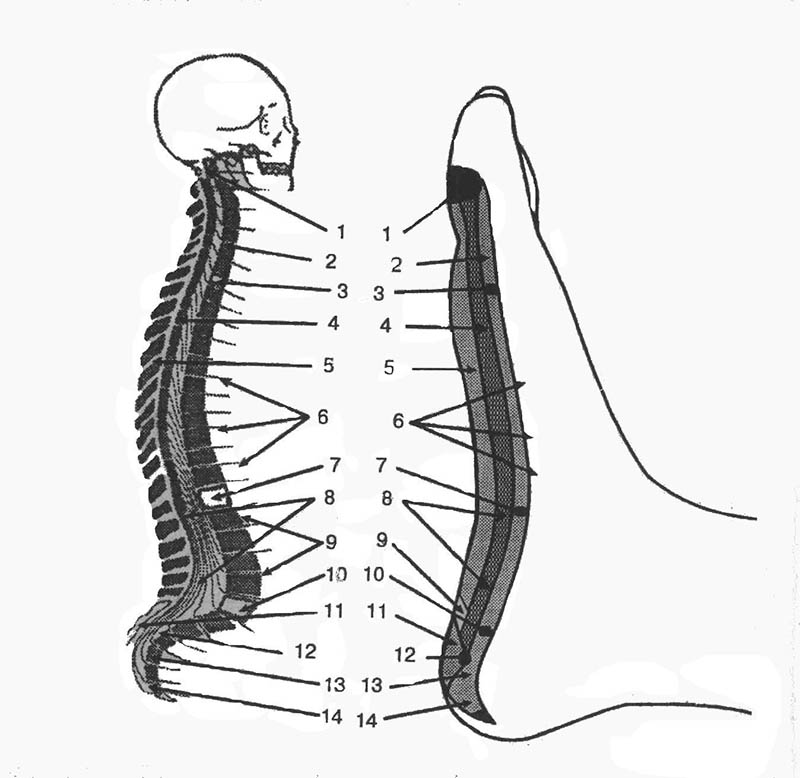
Figure 3 (inner surface of the foot - location of the spine).
- 1 cervical vertebra;
- spine, segments;
- 7 cervical vertebra;
- spinal cord;
- back muscles, spinous processes;
- exits of nerves, nerve endings;
- 12 thoracic vertebra;
- spinal canal;
- endings of the pelvic nerves;
- 5 lumbar vertebra;
- ilium, pelvic bones;
- bones of the sacrum;
- sacrum;
- coccyx;
Scheme of the main reflex zones of the feet
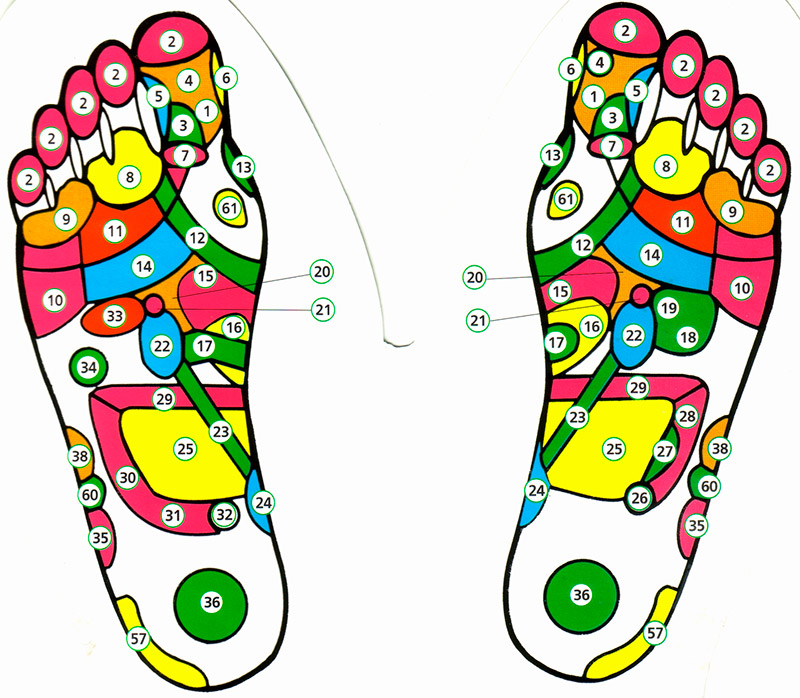
| LEFT FOOT 1. Head, brain (right side) 2. Frontal sinuses (right side) 3. Cerebellum, brain stem 4. Pituitary gland 5. Trigeminal nerve, right temple 6. Nose 7. Nape 8. Right eye 9. Right ear 10. Left shoulder 11. Trapezius muscle on the left 12. Thyroid gland 13. Parathyroid glands 14. Lungs and bronchi on the left 15. Stomach 16. Duodenum 17. Pancreas 20. Solar plexus 21. Adrenal gland on the left 22. Kidney left 23. Urinary tract left 24. Bladder 25. Small intestine 29. Transverse colon 30. Descending colon 31. Rectum 32. Anus 33. Heart 34. Spleen 35. Left knee joint 36. Sex glands on the left 38. Hip joint on the left 57. Nervous system 60. Lower leg on the left 61. Throat |
RIGHT FOOT 1. Head, brain (left side) 2. Frontal sinuses (left side) 3. Cerebellum, brain stem 4. Pituitary gland 5. Trigeminal nerve, left temple 6. Nose 7. Nape 8. Left eye 9. Left ear 10. Right shoulder 11. Trapezius muscle on the right 12. Thyroid gland 13. Parathyroid glands 14. Lungs and bronchi on the right 15. Stomach 16. Duodenum 17. Pancreas 18. Liver 19. Gallbladder 20. Solar plexus 21. Adrenal gland on the right 22 Kidney right 23. Urinary tract on the right 24. Bladder 25. Small intestine 26. Vermiform appendix 27. Ileum 28. Ascending colon 29. Transverse colon 35. Right knee joint 36. Sex glands on the right 38. Hip joint on the right 57. Nervous system 60. Lower leg on the right 61. Throat |
Additional reflex zones of the feet
They are located on the lateral (external and internal) and on the back surfaces of the feet.
Here, certain organs and systems, as well as “understudies” of the main sole zones, have their main reflex representation. They are used both for the treatment and prevention of various diseases, and to enhance the therapeutic effect on the main areas of the foot.
Inner surface of the foot
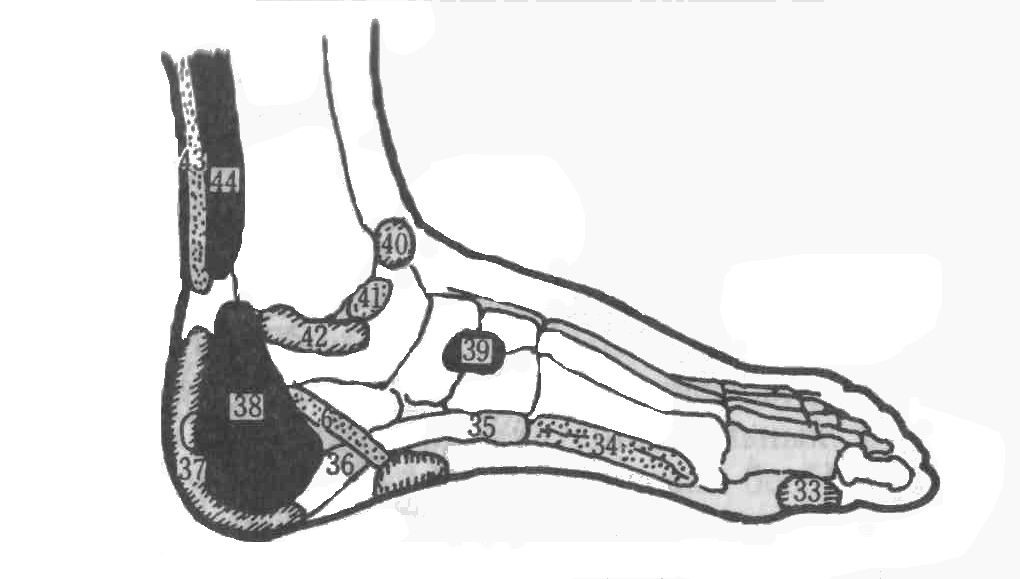
33. Cervical spine
34. Thoracic spine
35. Lumbar spine
36. Sacrum
37. Coccyx
38. Uterus or prostate gland
39. Rib
40. Groin
41. Lymph nodes of the lower half of the body
42. Hip joint
43. Rectum, anus
44. Sciatic nerve
Outer surface of the foot
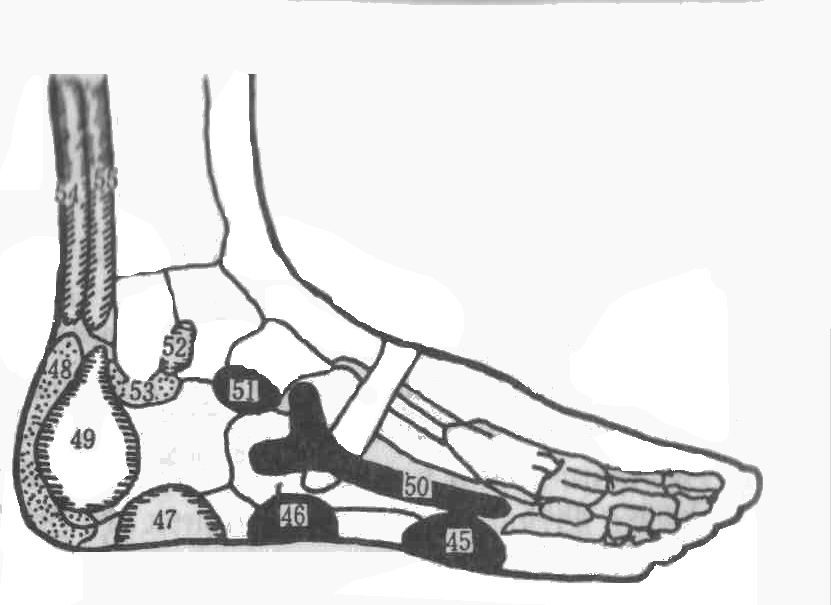
45. Shoulder
46. Elbow
47. Abdomen
48. Coccyx
49. Sex glands
50. Shoulder blade
51. Rib
52. Lymph nodes of the upper half of the body
53. Hip joint
54. Lower abdomen
55. Sciatic nerve
Reflex zones of the back of the foot
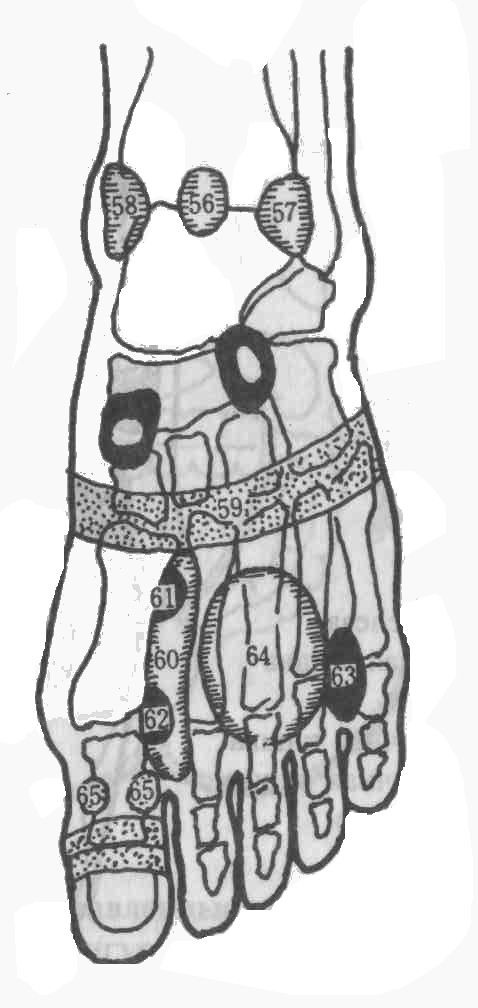
56. Center of the ankle joint
57. Lymph nodes of the upper half of the body
58. Lymph nodes of the lower half of the body
59. Diaphragm
60. Thymus gland
61. Trachea
62. Larynx
63. Ear labyrinth
64. Chest
65. Tonsils
66. Inferior palate
67. Upper palate
What do our feet tell us?
From time immemorial to the present day, according to the condition of the lower extremities, especially the feet, doctors judged the presence of certain deviations in the state of health. Every chronic disease, every untreated disease, even if it was many years ago, leave their traces. Of course, only a doctor can make a diagnosis, but the legs can provide invaluable assistance in finding out the causes of ailments and illnesses, help to conduct targeted treatment and effective prevention.
When examining the feet, you should pay attention to:
1. Changes in skin color.
The skin on the soles with a yellow tint indicates disorders in the liver, bladder, pancreas;
Brown - gray - blackish coloration is observed most often on the back of the foot. The causes are mainly metabolic disorders, long-term chronic disorders in the liver, as well as diseases of the veins and arteries;
Blue color indicates a tendency to convulsions and spasms, diseases of the veins;
Blue - red - this skin coloration is often observed in people suffering from gout or rheumatism, accompanies high blood pressure, high cholesterol in the blood and disruption of the small intestine;
General significant reddening of the skin on the feet can be determined by metabolic disorders, blood systems, respiration and the cardiovascular system;
Fragility or increased vascular permeability - hematomas of all colors, due to a pronounced underlying disease, or a neoplastic process.
2. Changes in skin temperature.
A healthy foot of a healthy person is dry and warm. Short-term deviations in one direction or another do not indicate a disease. Long-term changes may have reflex dependencies. For example: the right foot is warm, and the left cold - may indicate problems with the heart.
Wet and cold feet, "like a fish":
- predominantly lack of energy in the stomach, spasms (small intestine) of psychosomatic origin;
- mineral imbalances;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism).
Dry and cold - mainly indicate insufficiency of the cardiovascular system, as well as pathology of the brain and spinal cord (cerebral hemorrhage, transverse myelitis, etc.).
Wet and hot - indicate inflammatory processes occurring in the body, with an increase in temperature. Common in lung infections.
Dry and hot - energy redundancy:
- hormonal disorders (for example, excessive thyroid function);
- imbalance of mineral metabolism;
- disorders in the brain and spinal cord;
- gout (excessive acidity).
3. Changes in the structure of the skin.
Rough skin: thick or thin, it may look darkened or yellowish gray. Such changes are associated with chronic diseases of the mucous membranes, internal membranes of organs. Most often, roughness is observed on the back surface of the big toe, in the reflex zones of the nose, frontal and maxillary sinuses.
Smooth dried skin is observed with violations of the mineral balance. Easily damaged, ill, characterized by the frequent appearance of plaques similar to burns. Such skin is evidence of gout or rheumatism.
Rough skin around the ball of the thumb indicates chronic throat problems; along the lower edge of the posterior surface of the thumb pad - closely related to the bones of the skull (severe concussions, head injuries); under the 2 (3) metatarsal bone - evidence of a chronic disease of the bronchi and lungs (may appear in smokers).
Cracks can occur due to metabolic disorders or due to external influences (water or drying), especially on the heels.
4. The presence of folds.
More or less deep folds or wrinkles are meant. They can occur when there is a violation of the conduction of nerve impulses along the nerve fibers or damage to the nerves, in the presence of injuries and scars in the corresponding area of the body.
Cross creases: deep lines running across the sole across the inner edge of the toes. With such lines, the body indicates deformation of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis), old fractures of the vertebrae; about the presence of osteoporosis.
Folds on the sole of the foot: one or more folds between the 1st and 2nd fingers pass through the reflex zones of the thyroid gland - a direct evidence of the presence of a disease in this organ.
Transverse folds from the joint of the 4th toe of the left foot (heart zone) to the space between the 4th and 5th toes indicate disturbances in the functioning of the diaphragm or heart, as well as the consequences of lung diseases.
5. The presence of seals.
Along with superficial changes in the skin, there are also indurations in deeper tissues. They mostly appear in the form of nodules, primarily in muscles or tendons. For example, partial or general hardening of the tendon of the thumb indicates changes in the muscles of the back. The reflex zones of the short and long muscles of the back are located on the sole, near the inner edge, in the area of the thumb and up to the reflex zone of the bladder. The tension can be one-sided or two-sided. Strong retraction at this site indicates significant pressure between the vertebrae. Seals may also indicate psychological problems, in particular, psychosomatic pathology of the organs of the lower abdomen.
6. Examples of hormonal disorders:
- calluses on the pulp of the foot at the big toe appear with thyroid disorders;
- calluses on the heel on the sole, in the front of the heel indicate violations in the area of the gonads.
7. Nail changes.
Thickening ("wooden nails") - fragile, brittle nails; such nails are characteristic, first of all, in the pathology of the stomach, in metabolic disorders;
Deformity (crooked, claw-like nails, curved like watch glass) may be an indication of chronic brain damage as a consequence of traumatic brain injury.
8. Valgus deformity of the big toe - a very unpleasant deviation of the big toe - indicates family characteristics that are inherited. This disorder is associated with a predisposition to heart disease. In persons with such a pronounced defect, spinal deformities are often observed, which are already noticeable at a young age. Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland also contribute to the occurrence of such a deformation. At the same time, there are also violations of posture.
9. "Heel spurs" - very painful bone growths (exostoses) along the plantar contour of the calcaneus. They may indicate disorders in the urogenital region, leading primarily to an incorrect position of the spinal column and causing nervous reactions in the sacrum, coccyx and the area of \u200b\u200bthe intestines, anus and buttocks that are closely related to them.
Guidelines for the use of Lyapko application devices
Feet are a reflection of our body. Despite the fact that it is possible to act on isolated parts of the foot, the necessary effect of treatment or healing is achieved only when the reflex zones of both feet are affected. By covering all reflex zones, the treatment becomes "holistic". To use a holistic approach means to treat the whole organism. Not only the physical aspect is implied, but also the emotional and even spiritual. Experienced massage therapists and chiropractors always begin treatment of the spine with massage and foot correction.
Along with many medical preventive measures, the impact on the reflexogenic zones of the feet by multiple pricking of Lyapko's Insoles Plus is the best way to maintain, restore and improve health. The impact on the reflex zones of the foot awakens our “internal doctor” to action, gives us the fullness of natural sensations, imitating walking and running barefoot, defeats hypodynamia and its consequences.
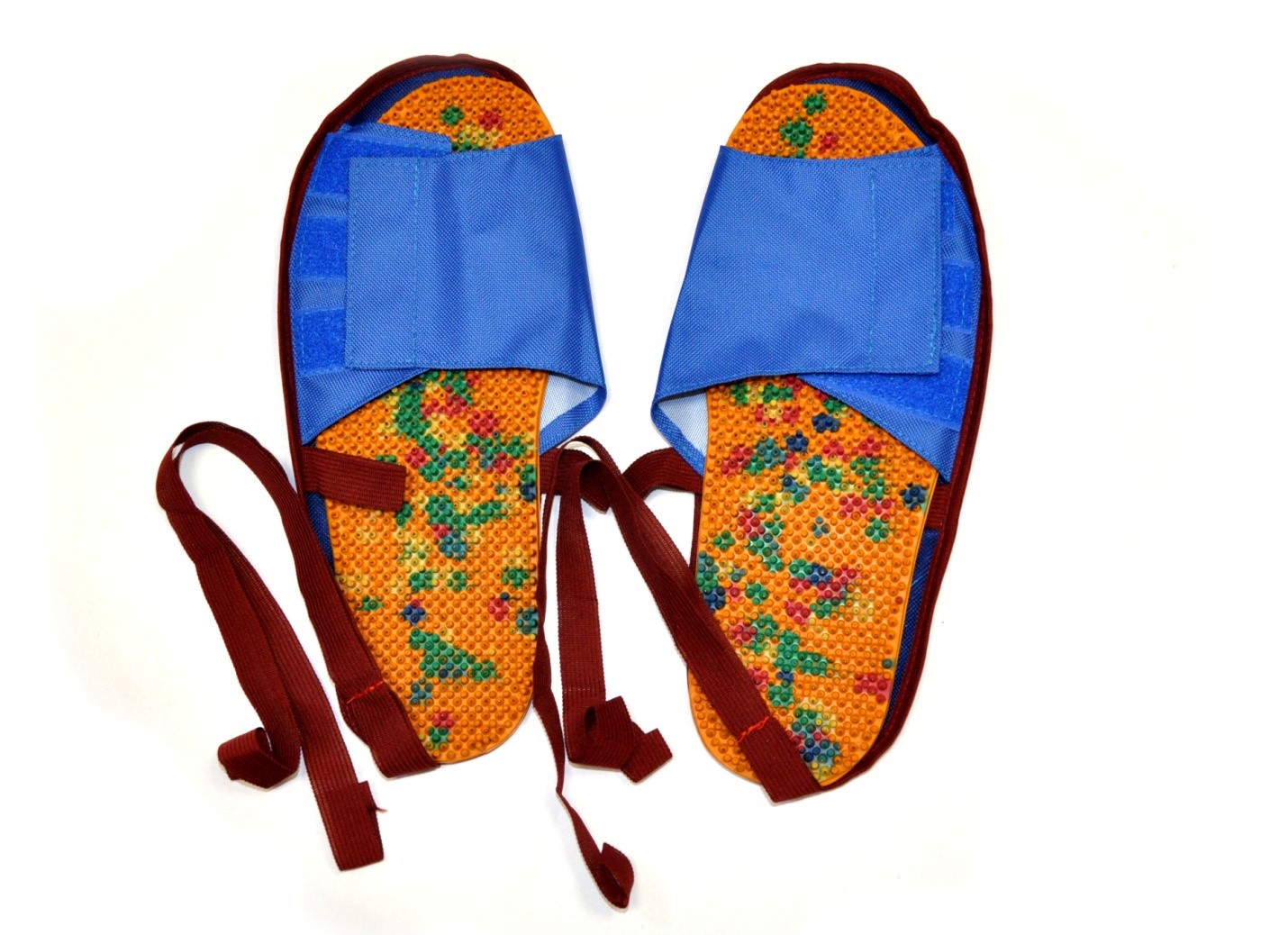

UAL "Insoles Plus" is an original and special applicator. A specially selected size of the restrictive columns individually doses and corrects the force of the needles on the reflexogenic zones of the sole, eliminating and preventing the possibility of damage to the skin. This is a wellness system that suits anyone and everyone, without age, gender and weight restrictions!
Needle insoles can be gently stepped on with the whole foot, you can stand and walk on them. In a sitting position, you can roll objects on the floor, massaging all the reflex zones.
To evenly press the insole to the foot, in the area of the arch of the foot, you need to put a cotton or gauze lining under it. Insoles must be purchased according to the size of the foot and more so that the fingers do not protrude beyond the foot, since there are very important biologically active points on the fingertips. We recommend focusing on the largest size in the family.
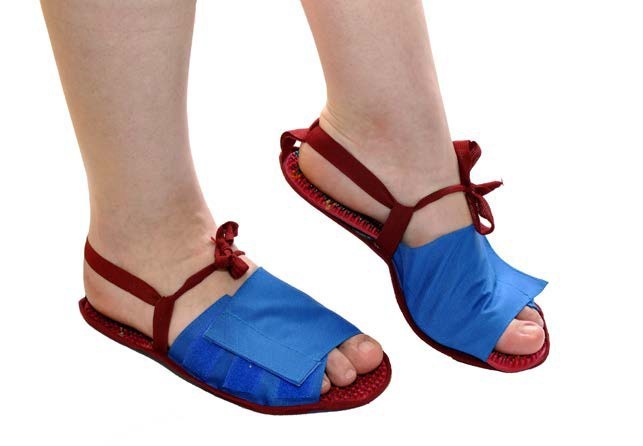

You can also use any flat applicator device on your feet, placing it on a pad or roller for better pressure.
For a more effective impact on the entire foot, it is recommended to use "Health Magic Tapes" 5-7-9 segment: wrapping the foot, starting from the fingertips and further to the required level.
It is definitely recommended to massage the feet with the “Pharaoh” and run them in with the “Big Roller M” , “Universal Roller M” .
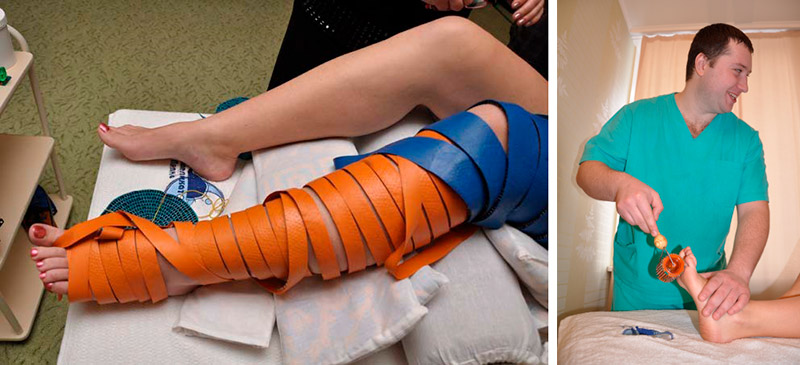
In health practices, the exposure time determines the desired effect:
- stimulating (tonic) effect - 5 - 7 - 10 minutes in the morning in an active motor mode (walking) - starting position - standing on insoles or intensive "rolling" of an object (rolling pin, tennis ball or glass bottle) with a foot with an insole. To save time on the insoles, you can take a shower, combine with foot baths.
- soothing (sedative) effect in the evening - 15 - 30 minutes of smooth, progressive, wavy movements of the foot on the insole or "delicate" rolling of the object - starting position - sitting on a chair or lying in bed.
In case of acute health disorders, it is necessary to influence the feet several times (3-5) a day for 5-7 minutes, paying attention to both the entire foot and individual reflex zones of the organs involved in the pathological process.
The treatment of chronic health disorders requires long-term exposure, both in terms of the duration of the session - 15 - 30 minutes 2 - 3 times a day, and in terms of the duration of the course - from several days to several months. To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to use in a complex way other static and dynamic types of Lyapko applicators on biologically active points and zones.
