Traumatic disease of the spinal cord
1 Traumatic disease of the spinal cord
2 Treatment of traumatic disease of the spinal cord
3 Rehabilitation treatment for spinal cord injuries
5 Experience in the application of Lyapko's application therapy in sanatorium-resort conditions.
Traumatic disease of the spinal cord
Spinal cord injury is one of the most severe types of injuries, which in many cases cause death, long-term disability, and permanent severe disability of the patient.
Traumatic disease of the spinal cord is a complex of reversible and irreversible abnormalities formed after a traumatic injury to the spinal cord, its membranes, nerve roots or blood vessels surrounding it. Usually, the disease is accompanied by pathological liquorodynamic and rheological changes, which entails disturbances in the passage of nerve impulses, loss of motor and sensory reflexes, and sometimes complete or partial immobilization of the body (paralysis).
Every year, thousands of people get spinal cord injuries, and approximately 80% of the total number of patients become disabled of group I or II. According to statistics, in about 60% of patients the condition of the disease remains unchanged for many years, in 25% there is a partial improvement in well-being, in 15% there is a sharp or gradual worsening of the condition.
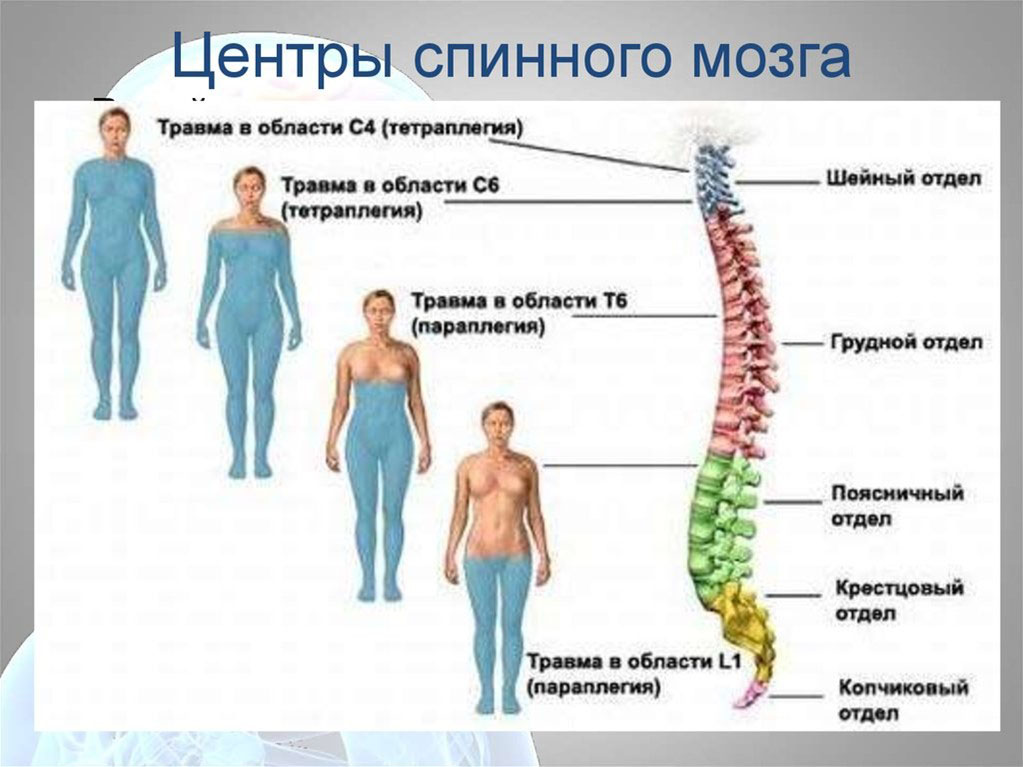
The spinal cord is a system of pathways (white matter) and communicative structures of segmental innervation (gray matter) that provide motor activity of muscles, sensitivity and coordination of body parts. If it is damaged or completely anatomically ruptured, starting from the level of injury, motor, sensory, trophic disorders develop, and the function of the pelvic organs is impaired. The severity of manifestations depends on the degree and level of damage to the spinal cord, and is also determined by the state of the hemodynamic system, respiration, and the neuropsychic sphere.
Traumatic disease of the spinal cord is an urgent and complex neurological problem, characterized by progressive disorders in the work of the main functional systems of the body - immune, hormonal, nervous.
Multisystem progressive disorders in such patients are explained by the limitation of motor activity due to a neurological disease, circulatory disorders due to physical inactivity and require a constant individual approach to each patient throughout the illness. The degree of manifestation of such disorders depends on the age of the patient, the nature and level of damage to the spinal cord, complications of injury and concomitant diseases.
Treatment of traumatic disease of the spinal cord
Rehabilitation after spinal cord injury can take a long time, and sometimes a lifetime. The duration of the recovery period will depend on the extent of tissue damage, as well as the general condition of the body.
The main difficulty in the treatment of traumatic diseases of the spinal cord is that nerve cells are not restored and the transmission of signals (impulses) from the proximal parts of the central nervous system to the peripheral motor parts passes through the area of damage. Thus, the signals simply do not reach the corresponding reflex areas.
With partial damage to the membranes of the brain or nerve roots, when some conductive fibers are preserved, additional interneurons are activated and new reflex connections are formed to replace the lost ones. New fibers fully or at least partially support the functionality of the body at the same level. In such cases, with prolonged physical training, it is possible to restore the motor abilities of the body.
With a complete rupture of the spinal cord, the passage of impulses is possible along extramedullary (bypass) pathways, but motor functions are not always restored. In addition, recovery from spinal injuries is quite slow, a long stay in a passive state, as it were, turns off some nerve circuits, although they are in normal working condition (similar to muscle atrophy if they are not used for a long time). Physical exercises on special simulators can save or restore the activity of paralyzed limbs.
Enhanced drug treatment is used in the acute period immediately after the patient has suffered an injury or surgery. Basically, these are painkillers, substances that relieve inflammation and stimulate the restoration of nervous activity.
Immediately in the postoperative ward, breathing exercises begin. Complexes of special physical therapy, light massage, passive and passive-active exercises to preserve muscle reflexes are added immediately after the patient recovers from spinal shock in the early period.
Numerous experiments and studies have shown that the impact on muscle tissue by passive or active actions, massages, functional electrical stimulation, wave methods, leads to the disinhibition of the activity of "dormant" motor neurons, promotes the regeneration of new nerve fibers in the injury zone and adjacent areas. Conversely, the complete absence of physical activity leads to muscular dystrophy and loss of neurological reflexes.
Rehabilitation treatment for spinal cord injuries
After stabilization of the patient's condition and completion of inpatient treatment, the attending physician prescribes rehabilitation (restorative) treatment. The number of procedures depends on the degree of damage and the level of brain damage, the general mood of the patient, his physical abilities, the desire to fight the disease and self-discipline in the implementation of individual training sessions.
Recovery of the spinal cord after injury consists of many activities. Rehabilitation begins as soon as possible. Rehabilitation activities include various physiotherapy procedures, physiotherapy exercises. Such patients are shown annual sanatorium treatment in specialized sanatoriums, in hospitals for rehabilitation treatment.
Physiotherapy treatment
Complex physiotherapeutic treatment is shown: electrophoresis, diadynamophoresis and ultraphonophoresis, galvanization, magnetotherapy, vibration stimulation, mud therapy, galvanic mud therapy, electrostatic massage, etc. Acupuncture, massage of biologically active points on the feet and palms, auricles, the use of Lyapko applicators in combination with other physiotherapy improve blood circulation and lymph flow, help raise the general tone of the patient's body, improve mood and add vitality in the fight against the disease. Good results in the treatment of traumatic spinal cord disease are shown by the parallel use of manual therapy.
Foot massage after a spinal cord injury allows you to normalize blood and lymph flow in the lower extremities, restore nerve conduction. The implementation of rehabilitation should be constantly monitored by specialists. It is necessary to monitor the body's response to ongoing therapy and make timely adjustments.
Physiotherapy
The task of physiotherapy exercises is general strengthening measures, ensuring functional and physiological positions, activation of the motor centers of the cortex, improving blood circulation in the area with impaired innervation.
The main principle in the use of physical exercises is: sequential movement from simple actions to more complex ones, a smooth increase in loads, systematic and continuous implementation of individual exercises. Teaching the function of maintaining balance, first in a sitting position, then standing with support (parallel bars, walkers, canes, crutches, etc.), moving in space, moving with obstacles (on steps).
Application therapy Lyapko
Lyapko's applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, applique belts, applique tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic possibilities. Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.

Mechanisms of action of the applicator
The high healing effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvano-electric;
- immunological.
A good effect is given by special classes in the pool in combination with application therapy (“Health Magic Ribbon”, “Baby” belt, “Universal M” belt).
The occurrence of galvanic currents upon contact of the applicators with the skin in the aquatic environment enhances the effects of superficial acupuncture.
The clinical effects of the method of multi-needle therapy are manifested in analgesic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, neurotrophic and immunomodulatory effects. Also in the regulation of the functions of the autonomic nervous system, the normalization of the processes of excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system.
How to work with the applicator, application zones
In 90% of cases, it is necessary to act on the pain zone, and to increase efficiency on additional and auxiliary zones.
It is always necessary to include the main zone (the region of the spine) in the general recipe.
Additional and auxiliary zones should be used when, for a number of reasons, it is impossible to influence the main zone (gypsum is applied, the wound surface). To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is advisable to include in the formulation the effect on the symmetrical zones of the healthy side.
The main zones are located on the back surface of the trunk, head, neck.
The main ones are named due to the fact that the skin areas on both sides of the spine and directly above the spine are closest to the exits of the roots of the cranial and spinal nerves and other structures.
Auxiliary zones: front surface of the trunk, head and neck.
Additional zones: zones of the skin of the lower and upper extremities, which are secondary (peripheral) in relation to the (central) structures of the spinal cord and brain.
Experience in the application of Lyapko's application therapy in sanatorium-resort conditions.
An important clinical manifestation of traumatic spinal cord disease is the development of osteoporosis, the intensity of which indicates the severity, rate of progression of the disease, and the adequacy of the rehabilitation.
Medical production company Lyapko on the basis of the specialized sanatorium named after Burdenko in Saki (Crimea) conducted research to study the effect of sanatorium-resort rehabilitation on bone tissue in this category of patients.
Depending on the treatment, TBCI patients were divided into 3 groups.
In all groups, treatment was generally accepted for this category of patients, which included:
- The sanatorium-and-spa regime is sparing or sparing-training.
- A complete balanced diet with a calcium content of at least 1000 mg / day.
- Calcemin
- Climatotherapy
- Therapeutic gymnastics
- Mechanotherapy
- Manual massage classic
- Electrical stimulation of weakened limb muscles
- psychotherapy
In the comparison group (GS) , applications of sulfide silt mud in the form of "underpants" were additionally used.
In group I , the generally accepted complex of sanatorium-and-spa rehabilitation was carried out with the use of mud therapy in the form of applications of a large area, more than 50% of the body surface - "trousers" and "back".
In group II , sanatorium-resort rehabilitation was carried out using multi-needle multi-metal applicators in combination with applications of therapeutic sulfide silt mud of a limited area, in the form of "underpants".
In all groups , rectal swabs of sulfide silt mud were used.
Lyapko's application therapy was carried out in 80 patients. Consisted of 30 procedures lasting 15 minutes. Application areas: back and plantar surface of the feet.
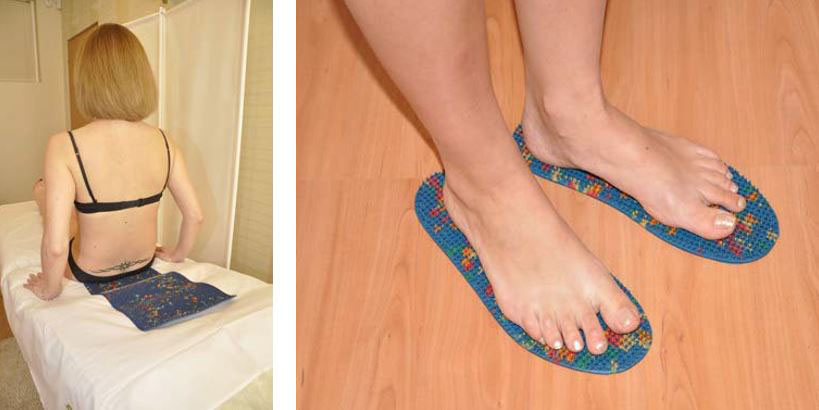
Scheme of application therapy Lyapko
The duration of the course is 2 months, it consisted of 30 complex procedures in 3 stages of 10 procedures with two inter-course breaks of 7 days each:
30 application packs on flat applicators (back, waist, buttocks - 15 minutes);
30 application impacts with the help of applicators-rollers on the area of the lower extremities.
"Big Roller M", "Universal Roller M" were used.
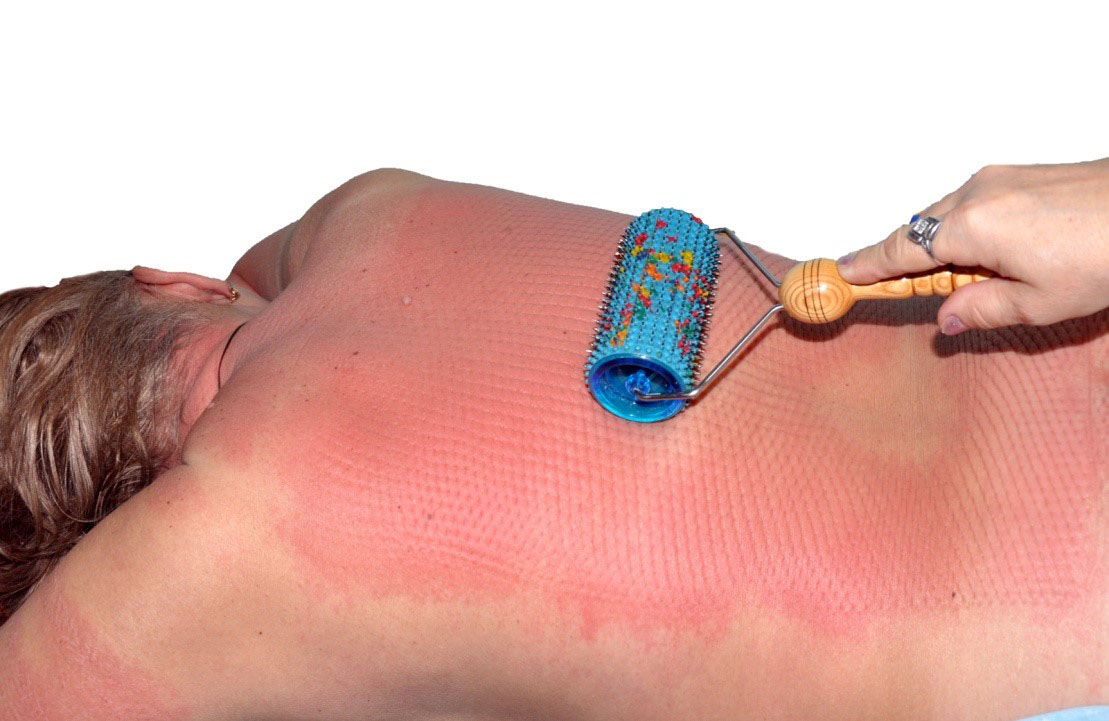
Flat applicators: “Large mat”, “Quadro”, “Chamomile M”, “Chance”, “Chance 6.2X4”, “Insoles plus”, “Needle massage pillow”.
To obtain a delicate effect when using applicators with a large step (7.0 and 6.2), depending on the sensitivity of the patient, procedures were performed through a thin cotton fabric.

Also, laying on applicators was used depending on the level of the lesion and symptoms.
If the lesion was in the cervical region, then flat applicators were placed on the neck, and the hands were rolled over. You can also apply “Magic Ribbons “Health” to your hands.
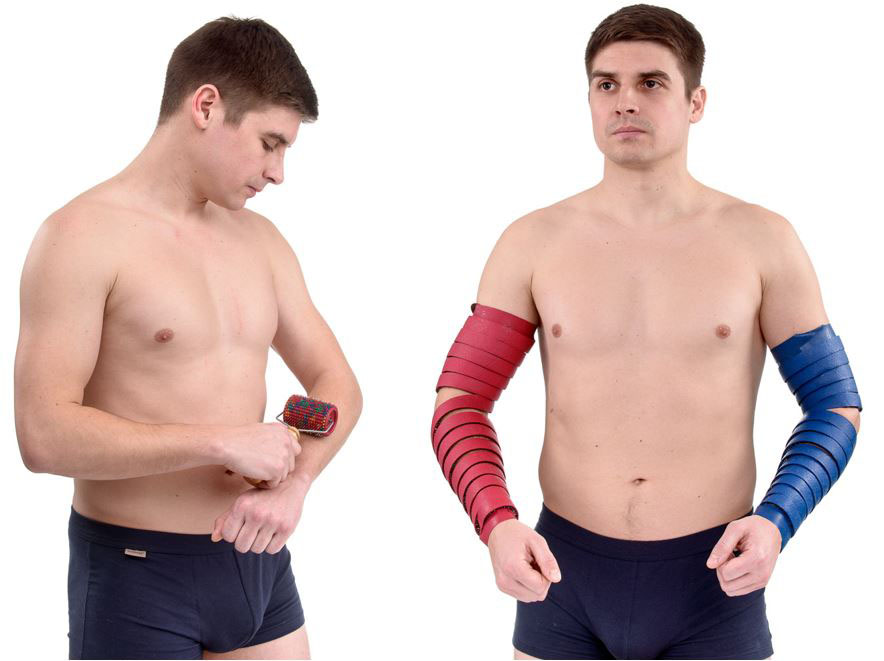
If the strength in the hands is broken, they put the “Big Roller M” into the palm and make pressure, roll the “Needle Ball” in the palms.

In case of urinary incontinence, the applicators were placed on the lower abdomen with a sand bag pressed against them.
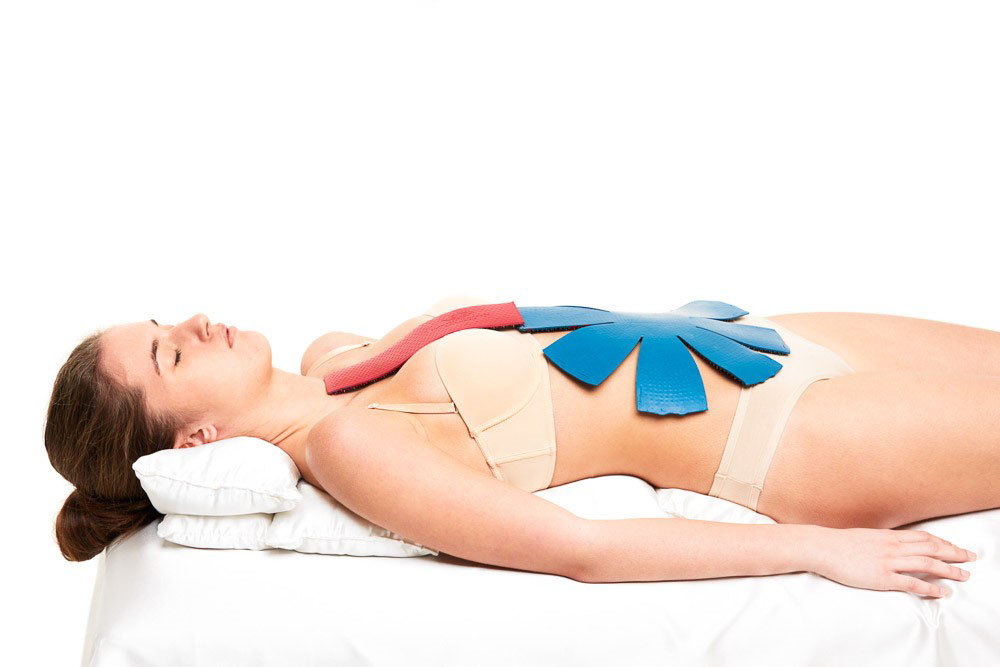
With a decrease or absence of potency, application therapy was performed on the perineum, lumbosacral zone with the capture of the buttocks, and the inner surfaces of the thighs were rolled over with a roller.
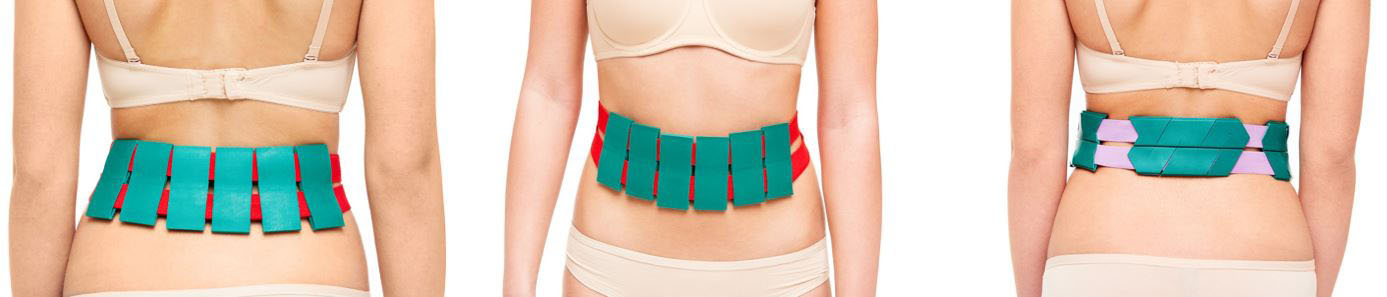
If the leg muscles were in good shape, applications were carried out on the lumbosacral zone with the capture of the buttocks, using the "Universal M" belt, the "Baby" belt, "Chamomile M". It is also recommended to use the “Magic Tape “Health” on the legs. On the feet on moistened skin, we used "Insoles Plus", rolled the legs for a long time, the procedure time was 20-30 minutes.

Against the background of complex sanatorium-and-spa treatment with the application of Lyapko's application therapy, the following results were obtained.
With coldness in the limbs and the absence of sensitivity in them, they began to warm up, sensitivity appeared or improved, sensations of “goosebumps”, tingling, a feeling of pulsation appeared, warmth went from the feet to the knees. There was a toning of atrophied muscles of the gluteal region and limbs.
With dry skin, increased sweating was noted. There was tenderness in the lower abdomen. Strengthened or in the absence appeared potency.
Some patients who used walkers, after a course of application therapy, began to gradually switch to independent movement.
After a course of application therapy, all patients showed an improvement in sleep (by 90%): they began to fall asleep better, the duration and quality of sleep increased, their mood improved, and a desire to live appeared.
Practical recommendations
Complex sanatorium-resort rehabilitation of patients with TBCI using multi-needle multi-metal applicators in combination with mud applications in the form of "pants" after 6-12 months of observation led to an increase in the bone tissue strength index. It was accompanied by positive changes in mineral metabolism and its hormonal regulation, which indicates the feasibility and necessity of such rehabilitation in this category of patients.
It is advisable to include annual osteodensitometry in the complex of examination of patients with traumatic spinal cord disease in order to identify and timely correct violations of the structural and functional state of the bone tissue and control treatment.
Patients with traumatic disease of the spinal cord at the sanatorium stage of rehabilitation are recommended to include the use of multi-needle different-metal applicators in the standard treatment complex.
The impact is carried out on the paravertebral zones at the level of the thoracic and lumbosacral spine and, consequently, on the feet. The technique is stable using applicators-plates with a needle pitch of 3.8-7.0 mm, selected individually. The total time of the procedure is from 14 to 30 minutes (the impact on each area is from 7 to 15 minutes) with a gradual increase in duration during the course of treatment. The course of treatment is 20-25 procedures performed every other day or daily. A second course of treatment with the use of multi-needle, multi-metal applicators is recommended after 2-3 months, up to 4 courses per year. It can be done on an outpatient basis.
conclusions
Ease of use of Lyapko application devices, safety allows disabled people to continue taking courses of such procedures at home. Now in the physiotherapy departments of many medical institutions, dispensaries, sanatoriums, Lyapko's application therapy is being carried out.
Many patients are contraindicated in electrophysiotherapy for various reasons. These are increased blood pressure figures, the presence of metal in the body (knitting needles, metal fragments), pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, etc. In these cases, Lyapko's application therapy is the means of choice.
In the physiotherapy departments of rehabilitation hospitals, patients with various pathologies are treated with Lyapko's application therapy. Such as: post-traumatic disease of the spinal cord, chronic sciatica, osteochondrosis of the spine, concussion, brain contusion, traumatic brain injury, post-stroke conditions, diabetes mellitus, pelvic fracture, post-traumatic encephalopathy, generalized arthritis, arthrosis, coxarthrosis, fractures limbs, injuries, bruises, etc.
When analyzing the main nosological forms of diseases among patients of the reflexology room of the physiotherapy department, an improvement in well-being was found in 98.4% of patients, no changes in 1.6%, no deterioration was detected.
It can be concluded that Lyapko's application therapy is highly effective in physiotherapy departments. Procedures patients can take further courses on their own at home.
