Respiratory diseases and application therapy Lyapko
Respiratory diseases include bronchitis, bronchial asthma, tracheitis, smoker's cough, SARS, pneumonia, emphysema, laryngotracheitis, etc. This is a common group of pathologies that affects people of any age and almost all year round.
In the autumn-winter period, these diseases are caused by various infections, and in the spring-summer period, most often by allergens.
1 Causes of respiratory diseases
2 Symptoms of respiratory diseases
3 Diagnosis of respiratory diseases
4 Treatment of respiratory diseases
5 Application therapy Lyapko in diseases of the respiratory system
Causes of respiratory diseases
- Infectious - caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi and can lead to bronchitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, SARS, etc.
- Allergic - in the presence of external allergens. Most often it is plant pollen, fungal spores, animal allergens, household allergens. They can lead to autoimmune diseases of the respiratory system, when the action of the immune system is directed to the tissues of its own body, which causes diseases such as bronchial asthma, etc.
- Provoke air pollution, household pollution, work in harmful working conditions, smoking (active and passive), adverse climatic conditions.
- Alcohol abuse, hypothermia, the presence of diseases of other organs and systems (diabetes mellitus, heart disease), the presence of foci of chronic infection, and many others.
Symptoms of respiratory diseases
- The most common symptom is shortness of breath, which can be different: during physical exertion, against the background of some kind of illness, with difficulty inhaling or exhaling, mixed.
- Cough: dry, wet, persistent or intermittent.
- Hemoptysis is a rare symptom, but characteristic only of respiratory diseases. It most often occurs with tuberculosis, cancer, or lung abscess.
- Pain sensations. Pain in different parts of the body: chest, throat, along the trachea.
Based on the symptoms, various diseases of the respiratory system are distinguished. Many of them can be both acute and chronic.
Diagnosis of respiratory diseases
Includes examination of the patient. With its help, a possible pathology of the shape of the chest is revealed, the type of breathing, its rhythm, depth and frequency are determined.
There are also instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- X-ray methods of research (fluoroscopy, radiography, tomography, bronchography, fluorography) are the most important in the diagnosis of respiratory diseases.
- Methods of functional diagnostics: spirography, spirometry.
- Laboratory research methods: microscopic examination of sputum, general and biochemical blood tests, general urinalysis.
Treatment of respiratory diseases
Treatment of respiratory diseases is prescribed individually, taking into account the identified diagnosis, the duration of the disease, the state of the immune system and the presence of concomitant diseases. For some diseases, treatment takes a couple of weeks, for others, treatment is taken for a long time and is aimed at reducing the severity of clinical symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations. Thirdly, the treatment is to prevent and strengthen the immune system.
The most common method of treating respiratory diseases is medication. Antimicrobial, antitoxic anti-inflammatory drugs, expectorants, antitussives, bronchodilators, painkillers, antihistamines are prescribed.
In cases where medical methods of treatment are ineffective and the pathology gives serious complications, they resort to surgical intervention.
Physiotherapy treatments
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment for diseases of the respiratory system occupy an important place, are prescribed depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of the main clinical syndromes.
Aimed at:
- stopping and accelerating the resolution of the inflammatory process;
- restoration of bronchial patency;
- elimination of bronchospasm;
- improvement of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract;
- restoration and improvement of the capabilities of the bronchopulmonary system;
- increased resistance to physical stress;
- prevention of exacerbations and achievement of long-term remission;
- preventing the progression of the disease and the development of irreversible changes in the lungs.
Contraindications to physiotherapy treatment:
- acute purulent inflammatory diseases of the lungs;
- lung abscess;
- pulmonary embolism;
- spontaneous pneumothorax;
- severe form of bronchial asthma;
- pulmonary heart failure II-III degree;
- general contraindications to the appointment of physical methods of treatment.
Apply: UVR on the chest area, UHF and UHF therapy, magnetotherapy, drug electrophoresis.
Mucolytic methods - the use of inhalations with mucolytic drugs.
Bronchodilator methods - in order to increase bronchial patency, nebulizer inhalations with bronchodilators are used.
Exercise therapy, breathing exercises, massage.
All types of reflexology: acupuncture, su-jok, electropuncture (impact on BAP with pulsed currents of low strength and low frequency), electromagnetic acupuncture (EHF), Lyapko's application therapy.
Application therapy Lyapko in diseases of the respiratory system
Lyapko's applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, applique belts, applique tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic possibilities.
Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
More detailed information can be obtained in the article "Lyapko applicators - mechanisms of action and application zones".

Application areas for pharyngitis, laryngitis, colds, bronchial asthma and other diseases of the bronchi and lungs (Fig. 1): main 2, 3; additional 1, 4, 12, 13; auxiliary 20, 22, 28, 31.
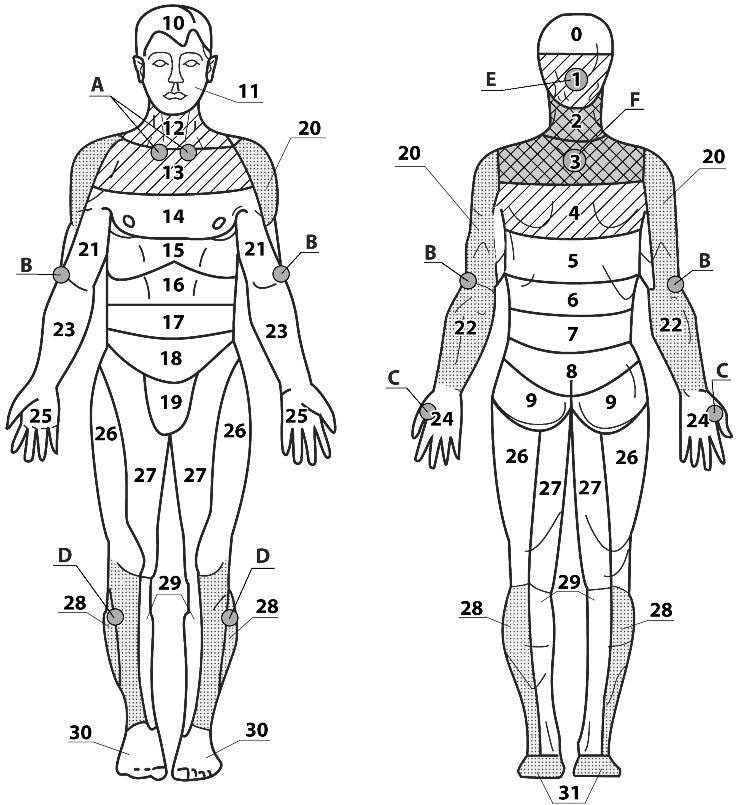
Fig.1
Procedures are performed in the absence of elevated body temperature.
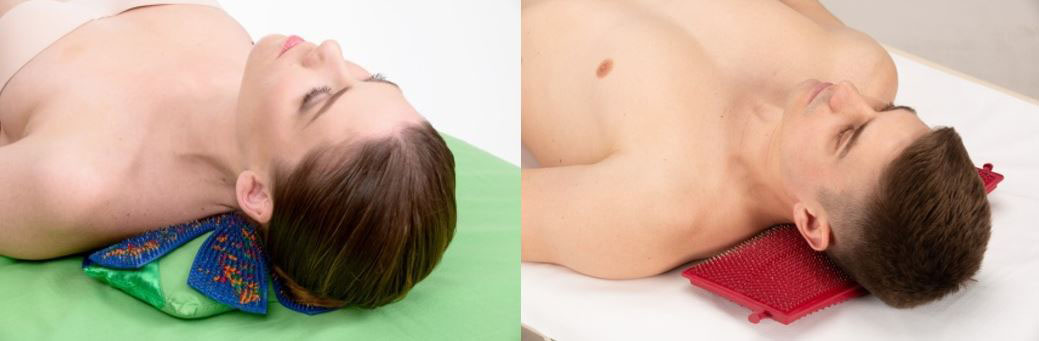
The following applicators are recommended. Flat applicators are used on the cervical-collar zone, on the area of the projection of the bronchi, lungs on the back: "Chamomile M", "Quadro", Needle massage pillow, "Chance", "Folk".
Also, flat applicators of large sizes - the larger the area of impact, the better the effect: Applicator "Large mat", "Massage needle large mat", "Chance 6.2x4".
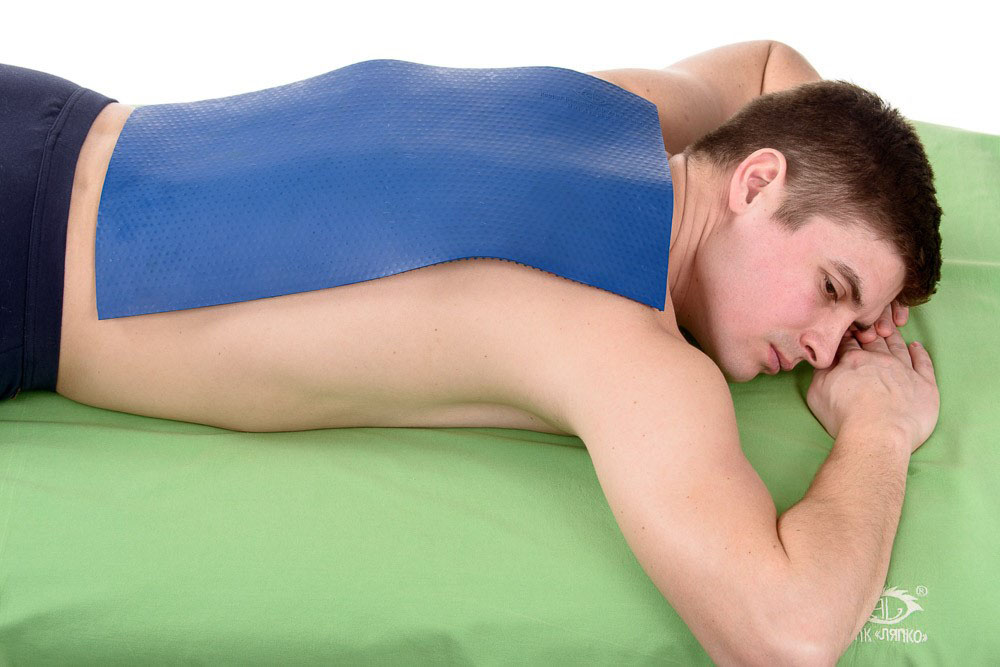

For colds, chronic diseases of the bronchi and lungs, the applicator is used as a “mustard plaster”, using applicators on the front surface of the body. Smaller applicators are used: "Chance", "Sputnik".
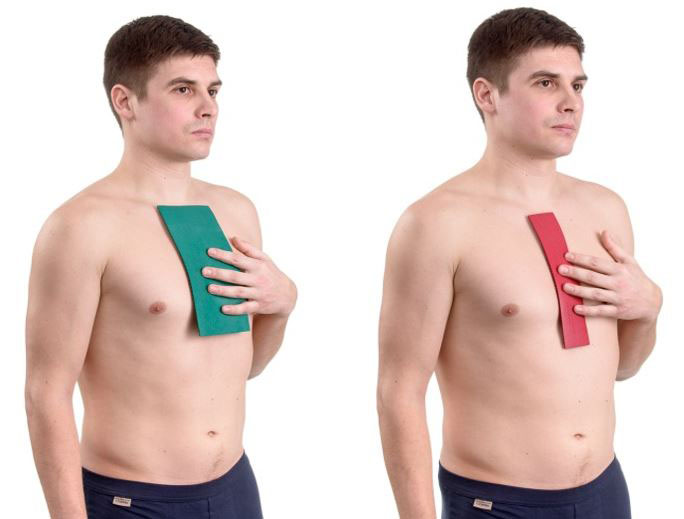
The applicators can be applied simultaneously or alternately to the area of the back and the anterior surface of the chest.
The exposure time is 20-30 minutes, the course of treatment is 10-14 days, which can be repeated after a break in 1-2 weeks.
To relieve an attack of bronchial asthma: lie down on any flat applicator with the main area (1, 2, 3)
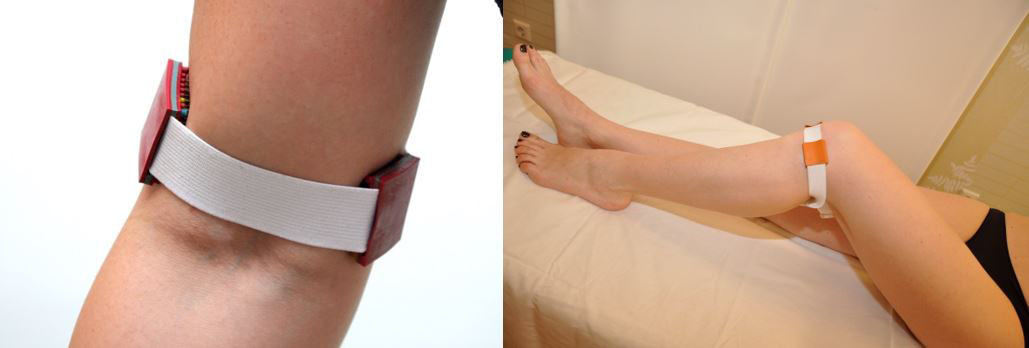
You can lie down or fix the application belts "Kid", "Sputnik" on these zones

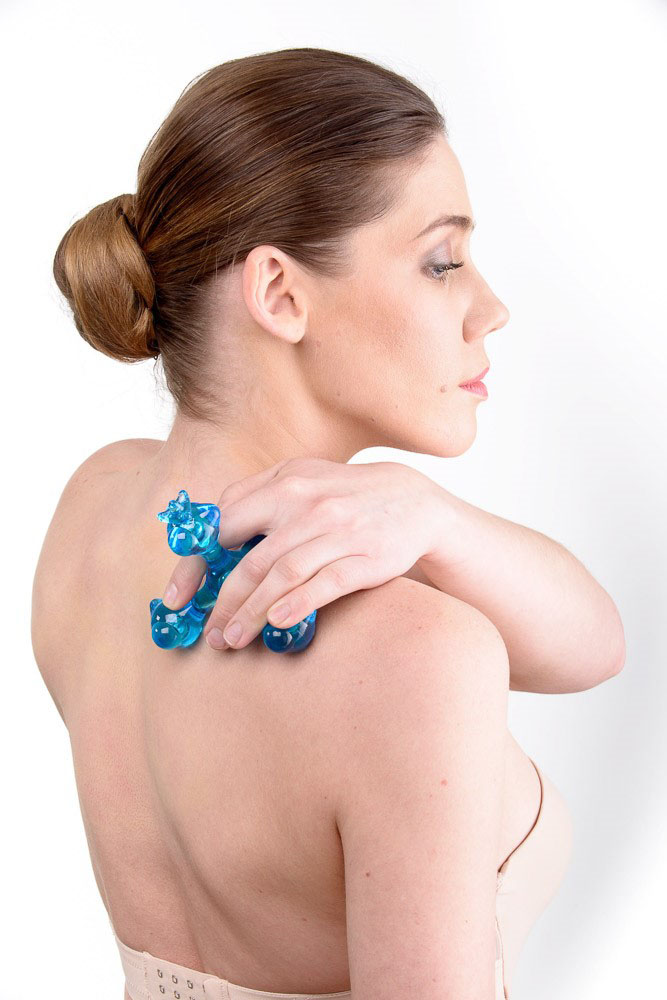
Simultaneously with the application "Large Roller M", "Universal Roller M" or a small applicator "Sputnik", "Chance" to carry out the impact in the upper sections of the anterior surface of the chest in zones 12 and 13 for 10-20 minutes.
In this case, it is necessary to hold back your breath, or at least breathe with a long exhalation through pursed lips.
For colds, bronchial asthma, it is recommended for a long time
(1-3 hours) work with small applicators "Kraplinka", "Kid" crosswise. For example, to the zone of point D on the left, to the zone of point C on the right, to the zone of point B on the left. To the zone of points A and E or F (Fig. 1)
In case of a runny nose, allergic or catarrhal rhinitis, lie on a small flat applicator in zone 1 or fix an application belt on this zone: "Baby" or "Universal M". The duration of exposure is 10-20 minutes, several times a day.
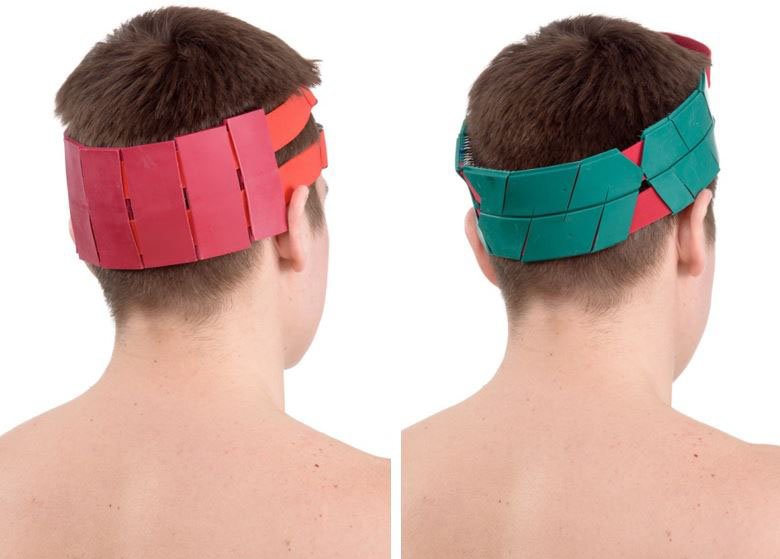
You can also use the belt "Magic Ribbon" Health "1p. 7-9 segment, which allows you to simultaneously act on the entire head area, capturing the main and auxiliary zones 1,2,12.
When wrapping the head with tape on sensitive areas (the area of the bridge of the nose and auricles), it is recommended to apply napkins in 1-2 layers. For better pressure on the back of the head, the procedure is best taken in a prone position.
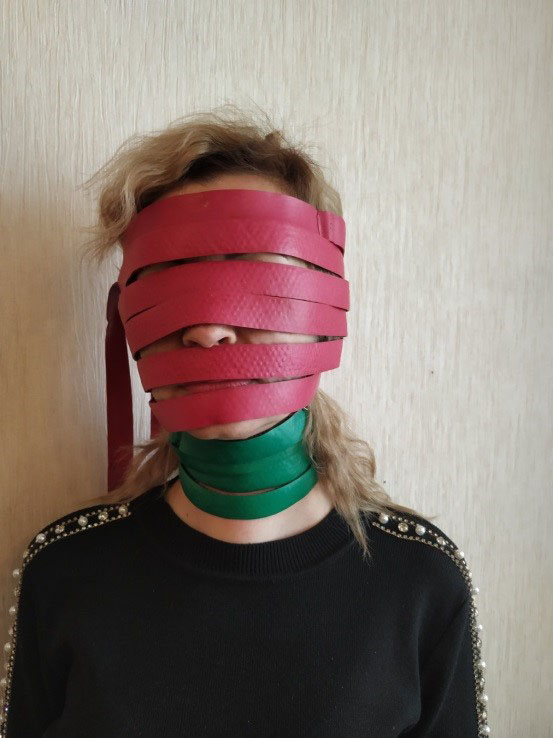

It is possible to process all these zones with a roller for 15-20 minutes.
All diseases of the respiratory system, especially those of an allergic nature, require breathing correction. It is necessary to regulate breathing in the direction of decreasing its intensity, holding it back (breathing must be silent, invisible). For this, the K.P. method is most suitable. Buteyko, pranayamas from the yoga system with long pauses after inhalation and exhalation, breathing through the Frolov apparatus, breathing under a thick blanket.
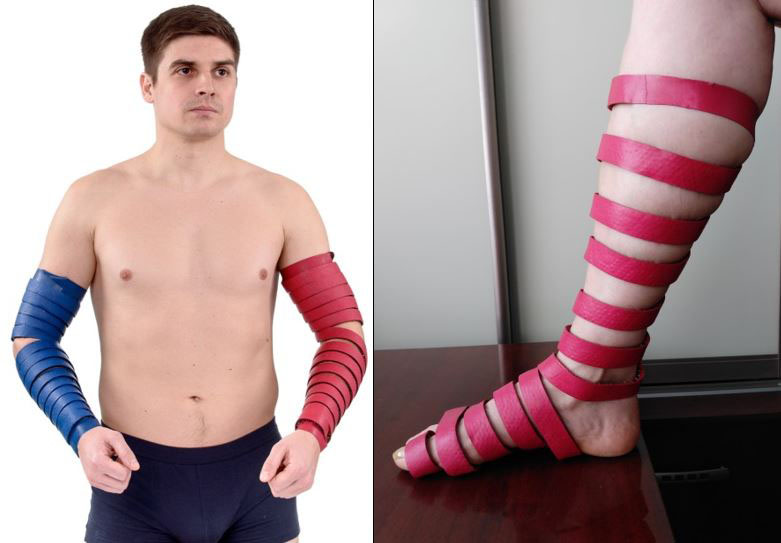
Auxiliary zones on the arms and legs can be treated with application rollers for 3-5 minutes or wrapped with the “Health Magic Tape” for 15-20 minutes.
The treatment always ends with the application of the feet. The feet can be warmed up and moistened before application (usually with colds, the feet feel cold and dry to the touch). To do this, 3-7 times a day, use a roller or applicator for 5-10 minutes.
You can gently step on the needle-shaped "Insoles Plus" with your whole foot, you can stand and walk on them. In a sitting position, you can roll objects on the floor, massaging all reflex zones.

To consolidate the effect after applying the applicators, it is useful to use rubbing with cedar, fir oil and other medicinal herbs.
Also, to improve the function of the bronchi and lungs, it is recommended to do a manual massage of the chest, as well as using the Pharaoh massager, which can be worked through a thin tissue or on a body lubricated with oil, cream for 10-15 minutes.