Applied Lyapko therapy in the treatment of prostatitis
What is prostatitis
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland.
The prostate gland (prostate) is located directly under the bladder. The urethra (urethra) passes through the thickness of the prostate gland. The inflammatory process that occurs in the prostate can immediately affect sexual function and urination.
According to statistics, prostatitis is one of the most common diseases of the male genitourinary system. With age, the likelihood of the disease increases, after 50 years, prostatitis is detected in 40% of men.
Causes of prostatitis
Prostatitis can be caused by various pathogenic infections. It can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia, etc.
The infection can enter the prostate gland in several ways:
- through the urethra - prostatitis, as a complication of urethritis (inflammation of the urethra);
- with lymph flow - the infection gets from the inflamed organs, primarily from the intestines, also after the transferred proctitis, hemorrhoids, dysbiosis;
- with blood flow - the infection can come from distant foci of inflammation, for example, with sinusitis or caries.
However, it is not infection that plays a decisive role in the onset of prostatitis. Infectious inflammation in the prostate gland usually develops against the background of factors conducive to the disease. Therefore, prostatitis can develop on its own, without infection. The main causes of prostatitis are stagnation of secretions in the prostate gland, as well as impaired blood circulation in the gland itself and its surrounding organs.
Stagnation of the secretion of the prostate gland and impaired blood circulation in the pelvic organs can lead to:
- prolonged sexual abstinence or excessive sexual activity, contributing to overstrain of the prostate gland;
- work, in a forced sitting position, sedentary lifestyle;
- chronic constipation.
Promote the penetration of infection into the prostate gland and increase the risk of prostatitis:
- prolonged stay in a state of stress, psychoemotional overstrain;
- hypothermia of the body;
- chronic alcoholism;
- decreased work of the immune system as a result of chronic infectious diseases, hard physical labor, chronic lack of sleep, poor nutrition, etc.
Complications of prostatitis
Prostatitis is dangerous with the complications that arise. Inflammation from a focus in the prostate gland can spread to other organs and cause:
- vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles);
- colliculitis (inflammation of the seminal tubercle);
- epididymo-orchitis (inflammation of the testicles and their appendages).
If prostatitis is left untreated, it can lead to male infertility.
Symptoms of prostatitis
The main symptoms of prostatitis are:
- soreness in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region, in the groin, in the perineum and genitals;
- increased urination;
- Difficulty urinating, incomplete emptying of the bladder due to prostate edema;
- sexual dysfunction.
Disorders of the genitourinary system often lead to neurasthenia.
Less often, prostatitis can occur in an acute form with high fever, severe symptoms, with acute pain.
But most often chronic prostatitis develops.
Chronic prostatitis can occur with mild symptoms, which may not cause much concern for a long time. Often it is first detected only during a routine examination. The temperature is kept within normal limits. Patients may periodically experience discomfort in the perineum, during urination and defecation. During bowel movements, discharge from the urethra can be observed - this is a characteristic symptom of chronic prostatitis.
The development of chronic prostatitis leads to problems with erection.
Currently, the significance of the consequences of this disease is determined not only by bodily suffering, but also by a pronounced decrease in the quality of life, which can be comparable with patients who have suffered myocardial infarction.
Diagnostics of the prostatitis
After digital rectal examination of the prostate gland, an ultrasound of the prostate gland and laboratory tests are prescribed: analysis of prostate secretion, general urine analysis, general blood test.
Treatment
The basic principle of prostatitis treatment: an individual approach, taking into account the characteristics of a particular patient
Chronic prostatitis treatment is a lengthy process. It is important to adhere to the principle of individuality, optimal therapy, and on the part of the patient - complete trust in the doctor's actions, the courage to withstand certain restrictions and even the willingness to eliminate bad habits. The chronic course of prostatitis has a stage of remission, attenuation of symptoms. Both the doctor and the patient need to remember that the period of remission may end, and then there is a threat of exacerbation of prostatitis.
In the treatment of chronic prostatitis, the main role belongs to antibiotic therapy. During therapy, massage of the prostate gland, hot microclysters of 100 ml of water (decoctions of chamomile or sage, heated to a temperature of 40–41 ° C), physiotherapy (inductometry, ultrasound, electrophoresis, Lyapko's application therapy) are shown.
Diet therapy
In case of prostate disease, you should strictly follow a diet with the exception of spices, canned food, smoked meats, alcohol and beer. Zinc-rich foods are very useful - pumpkin seeds, nuts, peas, cereals and beans. Zinc is known to shrink the prostate gland and reduce symptoms of the disease in some people. In addition, zinc deficiency is associated with a predisposition to prostate cancer. One of the richest sources of zinc and essential fatty acids is pumpkin seeds.
Physical therapy in the treatment of prostatitis is used in different ways. Its action is aimed at enhancing blood circulation in the pelvic organs, which increases the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. For physiotherapy, electromagnetic oscillations, ultrasonic waves, laser exposure, Lyapko's application therapy are used.
Lyapko application therapy
Lyapko applicators in various modifications (plates, rollers, applique belts, applique tapes) are an original, powerful device with many health-improving therapeutic capabilities.

Their action is based on the principles of traditional Chinese medicine - superficial multi-needle acupuncture, as well as on the general physiological mechanisms of life.
Applicator mechanisms of action
The high health-improving effect of Lyapko applicators is due to a combination of intense reactions:
- reflex-mechanical;
- galvanic-electrical;
- immunological.
Application therapy has a pronounced analgesic and antispasmodic effect. Improves blood circulation, lymph flow, microcirculation, reduces tissue edema. It activates the tissue mechanisms of immune defense, increases the level of its own opiate peptides and antistress hormones in the blood, reduces the sensitivity of pain receptors, has a positive psychoemotional effect and, as a result, stimulates the general adaptive mechanisms of a person. Contacting the skin, the applicator's needles stimulate the release of a person's internal drugs, including his “internal doctor” in the work.
It is important to note that local (local) improvement of blood circulation during application therapy occurs without additional stress on the heart, since the work of the peripheral circulation is enhanced, and the heart is resting at this time. This is very important for all categories of patients and, especially, with ischemic heart disease, circulatory failure of 1-2 degrees, and elderly people.
The convenience of Lyapko's application therapy is that it can be carried out at home, according to methodological recommendations. Especially if it is not possible to carry out physiotherapy in a medical institution or there are contraindications to electrophysiotherapy. In addition, the applicator needles contain zinc, which is so necessary for the normalization of prostate function. It can be used in combination with medication, which gives a good effect.
How to work with the applicator, application zones
In 90% of cases, it is necessary to act on the pain zone, and to increase efficiency on additional and auxiliary zones.
It is always necessary to include the main zone (spine) in the general recipe.
The main zones are located on the back of the body, head, neck. The main ones are named due to the fact that the skin areas on both sides of the spine and directly above the spine are most closely located from the exits of the roots of the cranial and spinal nerves and other structures.
Very important meridians also pass here, which affect all organs and systems of the body in the region of which they pass, control the protective energy of a person, and affect his resistance to diseases.
Auxiliary zones are the anterior surface of the torso, head and neck. The result is achieved faster when using auxiliary zones simultaneously with the main and auxiliary zones.
Additional zones : skin zones of the lower and upper extremities, which are secondary (peripheral) in relation to the (central) structures of the spinal cord and brain.
On the inner and outer surfaces of the arms and legs, there are zones of "Yin" (female) and "Yansky" (male) groups of channels - the meridians of organs located on a certain surface of the arms and legs, and having various groups of points that differ in purpose.
Using for applications and acting on various groups of points of certain channels of the meridians, we have the opportunity to additionally regulate (change, increase or decrease) the activity of certain organs and systems (general action). We intensify the work during the application of Lyapko applicators to the main and auxiliary zones and additionally provide a therapeutic effect.
Thus, the result is achieved faster when using the main zones simultaneously with additional and auxiliary zones, or if it is not possible, then alternately.
Application areas for the prostate:
- basic 8.9;
- additional 7, 18,19;
- auxiliary 27, 29, 30, 31, (23, 25). (Fig. 1)
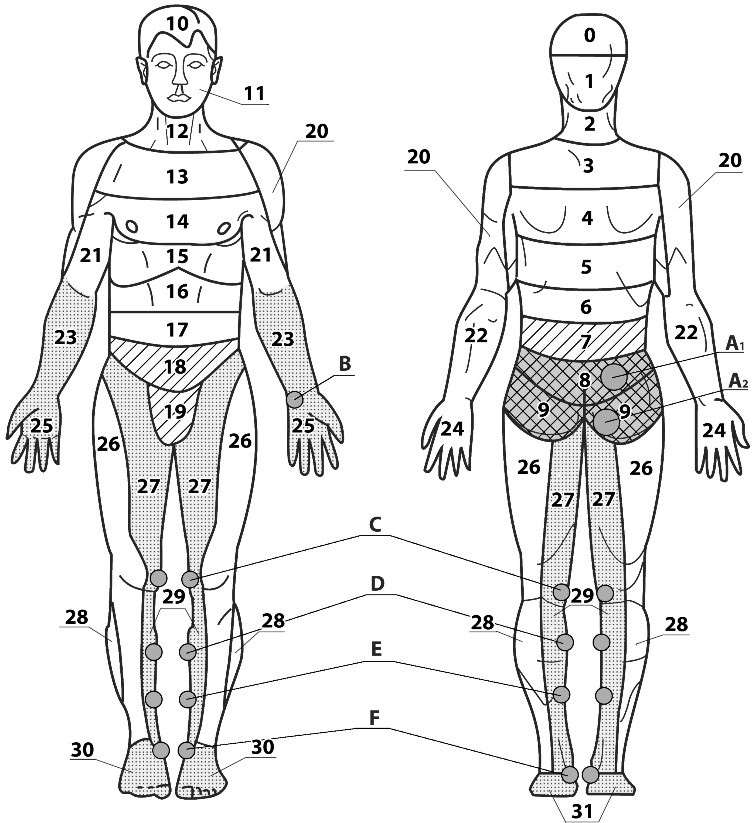
Fig. 1
Variants of Lyapko's application devices for the lumbar and sacro-gluteal region, as well as the lower abdomen (main and additional zones):
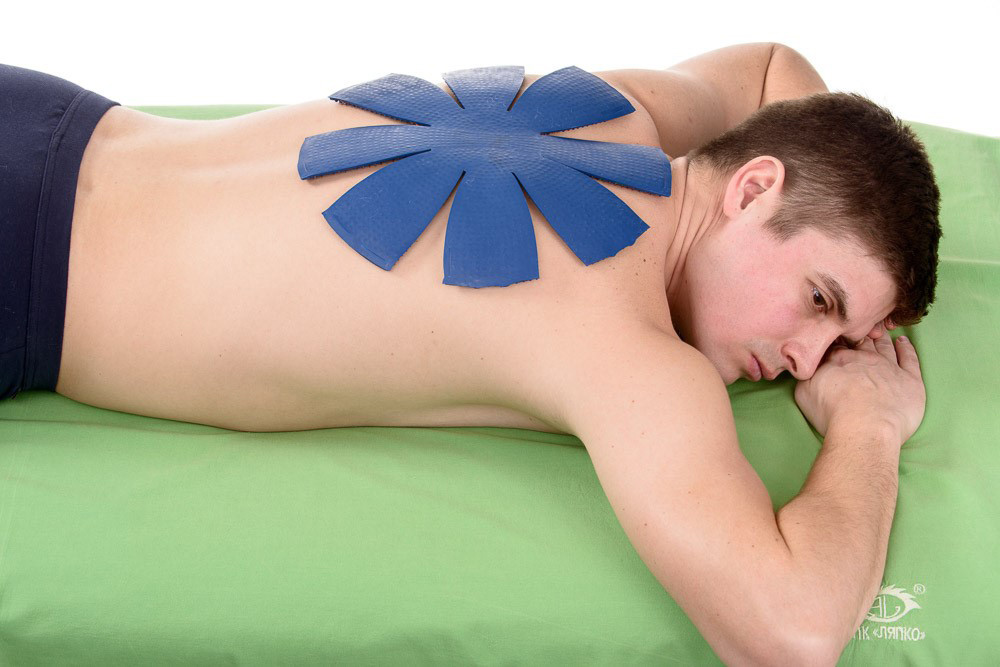
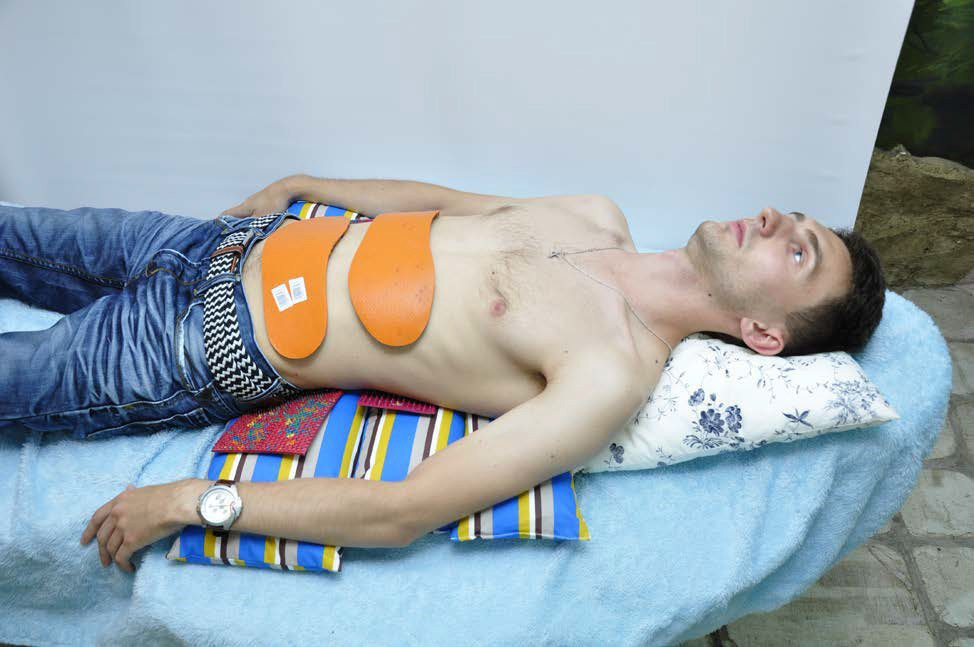
Flat applicators "Chamomile M" , "Insoles plus" , "Quadro" , "Chance" , which are used in the lying position on zones 7, 8, 9

or on the lower abdomen and pubic region to the area 18.19.
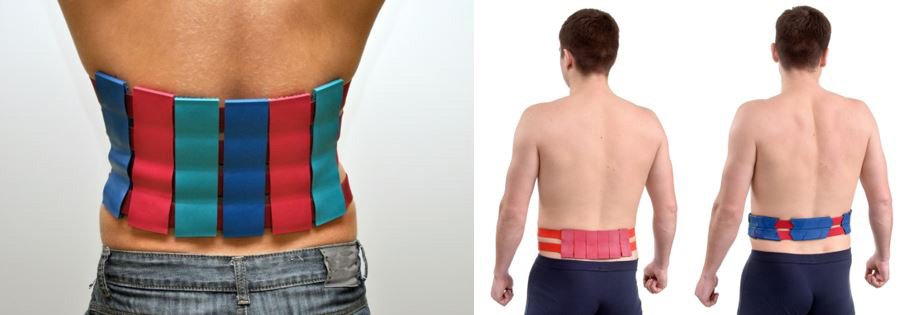
It can be used in the supine position or fix these zones Belt "Satellite" , Belt "Baby" , "Belt universal M" . The exposure time is 20-30 minutes.
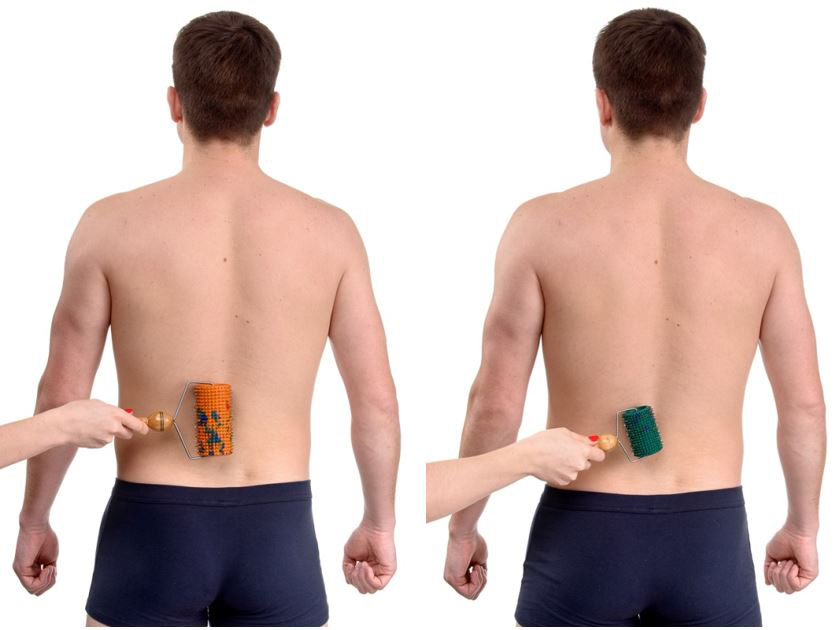
Run-in with "Large roller M" , "Universal roller M", "Face roller M" zones 7, 8, 9, 18, 19. The exposure time is 10-12 minutes.
Belt "magic tape" Health " 1 cavitary, 1H + 1H 7-9 pelvis segment is wrapped with capture zones 7, 8, 9, 18, 19 for 20-30 minutes.

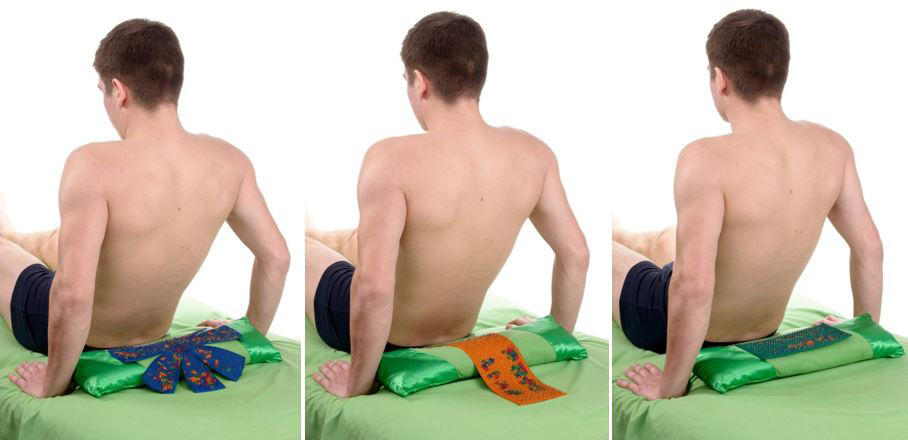
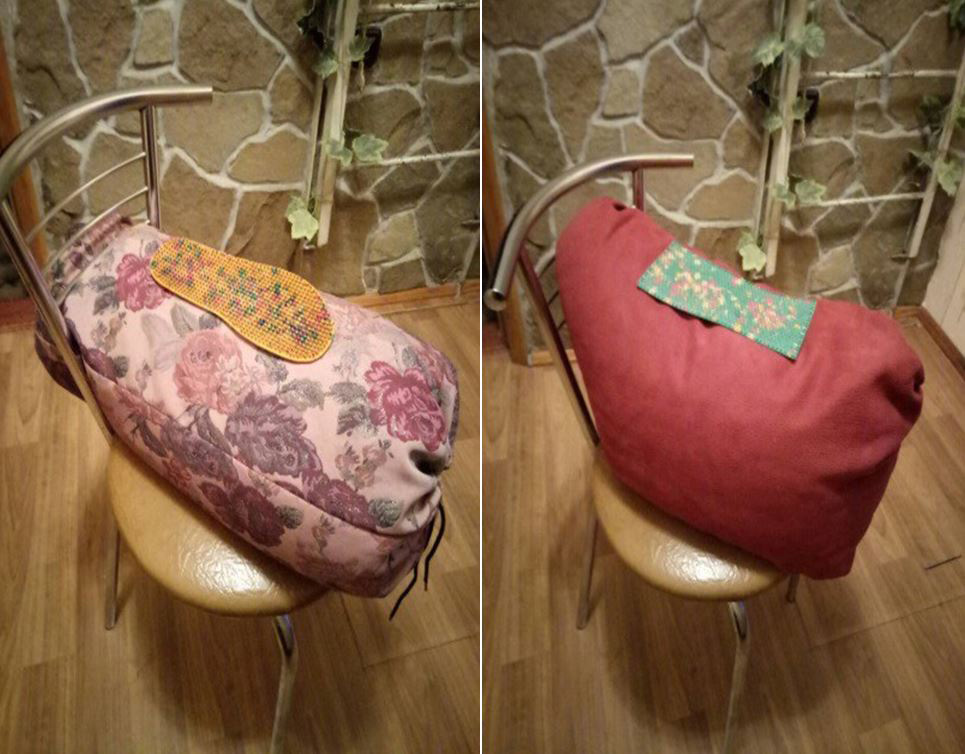
Use small applicators: "Chance" , "Insoles Plus" , "Sputnik Plus" to act on the perineal area in a sitting position. To do this, put a pillow vertically on a chair, an applicator on top and sit, like on a horse, naked or through linen. Adjust the pressure force independently according to the comfort of sensations. Exposure time 15-20 minutes 1-2 times a day (more frequent can lead to exacerbation).

Applicator options for auxiliary zones:
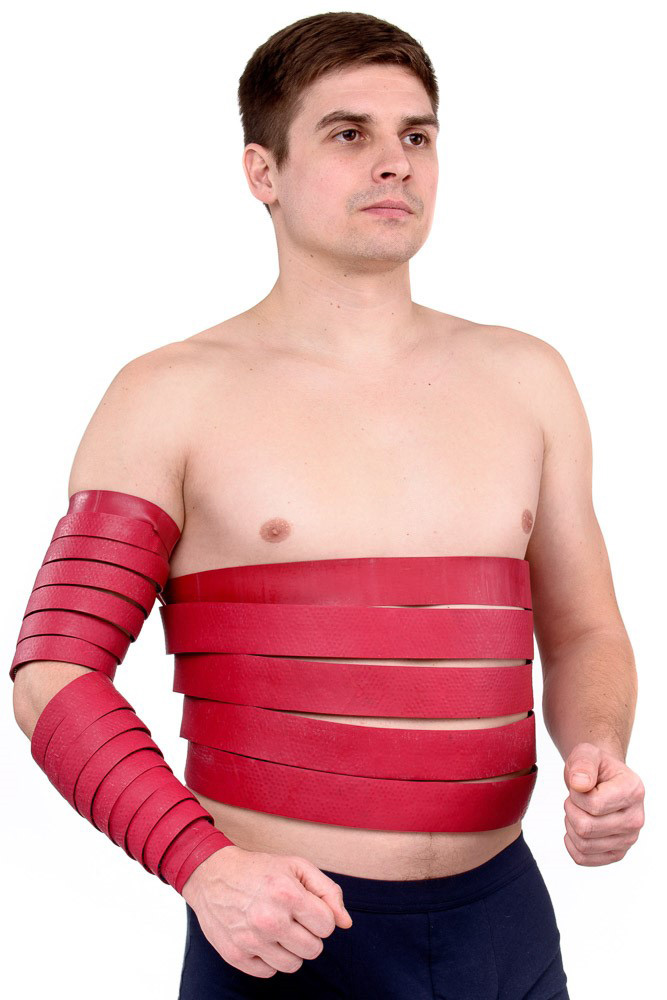
Belt "Magic tape" Health "1 cavity, 1p + 1p, 1 + 2 5–7–9 segment arms are wrapped with a capture of zones 23, 25; legs of zones 27, 29, 30,31. The exposure time is 20-30 minutes.
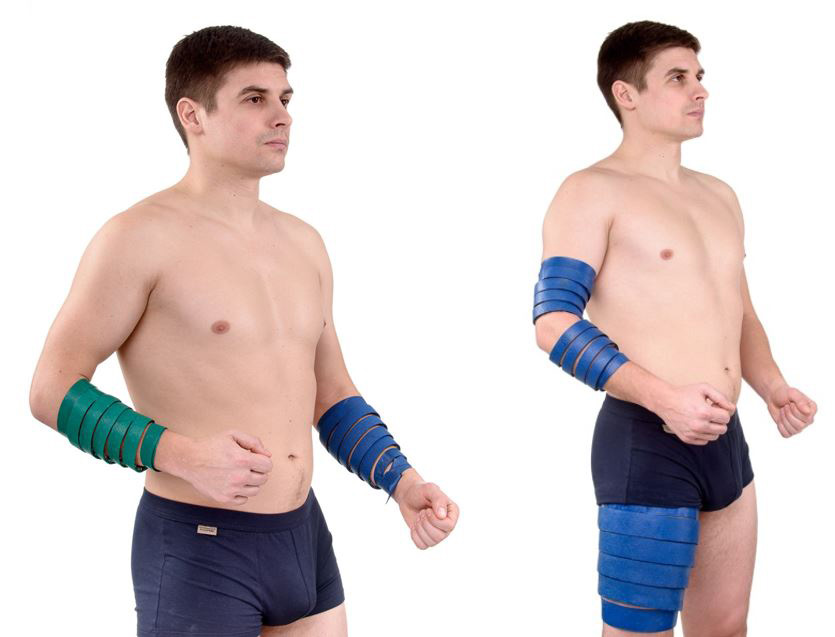
Run-in with the "Large roller M" , "Universal roller M" , "Face roller M" zones 23, 25 on the hands; on legs 27, 28, 30, 31 Exposure time 10 -12 minutes.
"Plus insoles" on the feet - zone 31. The exposure time is 15–20 minutes.

To improve the psycho-emotional state, to relieve stress, it is recommended to apply applicators to the cervical-collar zone (stress zone), to the interscapular region for 20-30 minutes. To do this, you can use the Camomile M applicator or other flat applicators .

